DIY Closet Shelves: The Hidden Psychology and Physics That Make or Break Your Storage System
Building effective DIY closet shelves requires understanding both human behavior and material science principles. While pre-made DIY closet storage can be in the $650 to $950 price range according to DIY Pete, a well-planned custom system can be built for under $400 while delivering superior functionality tailored to your specific needs and usage patterns.
Table of Contents
-
The Psychology Behind Successful Closet Organization
-
Understanding Load Distribution and Material Science
-
Strategic Installation Planning for Long-Term Success
-
Simple Construction Methods That Outperform Complex Designs
-
Installation Sequencing to Avoid Costly Mistakes
-
Predicting and Preventing Future Maintenance Issues
-
How Professional Decluttering Services Support Your DIY Success
TL;DR
-
Your brain processes closet organization in predictable patterns – design shelves that work with these natural tendencies, not against them
-
Most DIY shelf failures happen because people misunderstand how weight travels through the system over months and years of daily use
-
Professional contractors think in decades, not weekends – plan your installation with future modifications and removal in mind
-
Simple construction techniques using three materials or fewer often outperform complex systems in both function and durability
-
Install components in the right sequence to maintain access for adjustments and prevent having to redo completed work
-
Different shelf areas wear out at different rates – plan maintenance schedules based on usage patterns rather than waiting for problems
The Psychology Behind Successful Closet Organization
Your closet shelving system creates a behavioral ecosystem that either supports or undermines your daily routines. Understanding how your brain processes visual information and makes decisions determines whether your DIY closet shelves become a long-term organizational success or another abandoned system. The key lies in designing shelves that work with natural psychological patterns rather than fighting against them.
Decision fatigue occurs when your brain has to process too many visual choices – poorly designed shelving creates this problem every time you open your closet door. I’ve seen countless people abandon perfectly functional storage systems because they required too much mental energy to maintain. The 7-second rule governs organization success: systems requiring more than seven seconds of decision-making per item retrieval get abandoned by most people.
Visual weight distribution affects behavior regardless of actual weight – darker colors and bulkier shapes naturally want to occupy lower shelf positions. This psychological tendency influences where people naturally want to place items, and fighting against it creates ongoing friction in your system.
How Your Brain Processes Closet Decisions
Cognitive load directly impacts how successfully you’ll maintain any organizational system. Your brain follows predictable patterns when processing visual information, and shelf design either reduces or increases the mental effort required for daily clothing decisions. When learning how to make closet shelves DIY, understanding these cognitive patterns becomes crucial for long-term success.
Visual processing happens in milliseconds, but decision-making about item placement can create bottlenecks that lead to system abandonment. Items perceived as visually “heavier” migrate toward lower shelves over time, regardless of their actual physical weight. Color contrast and shape recognition play larger roles in organization success than most people realize.
“One of the most intimidating parts of closet organization is deciding where to begin” according to Architectural Digest, highlighting how decision paralysis affects even the initial stages of closet organization projects.
The Seven-Second Decision Threshold
Most people abandon organizational systems that require more than seven seconds of decision-making per item retrieval. This threshold determines whether your DIY closet shelves design supports quick daily routines or creates friction that leads to clutter accumulation.
Decision time increases exponentially when visual cues don’t clearly indicate where items belong. Complex categorization systems fail because they exceed the brain’s quick-processing capabilities during rushed morning routines.
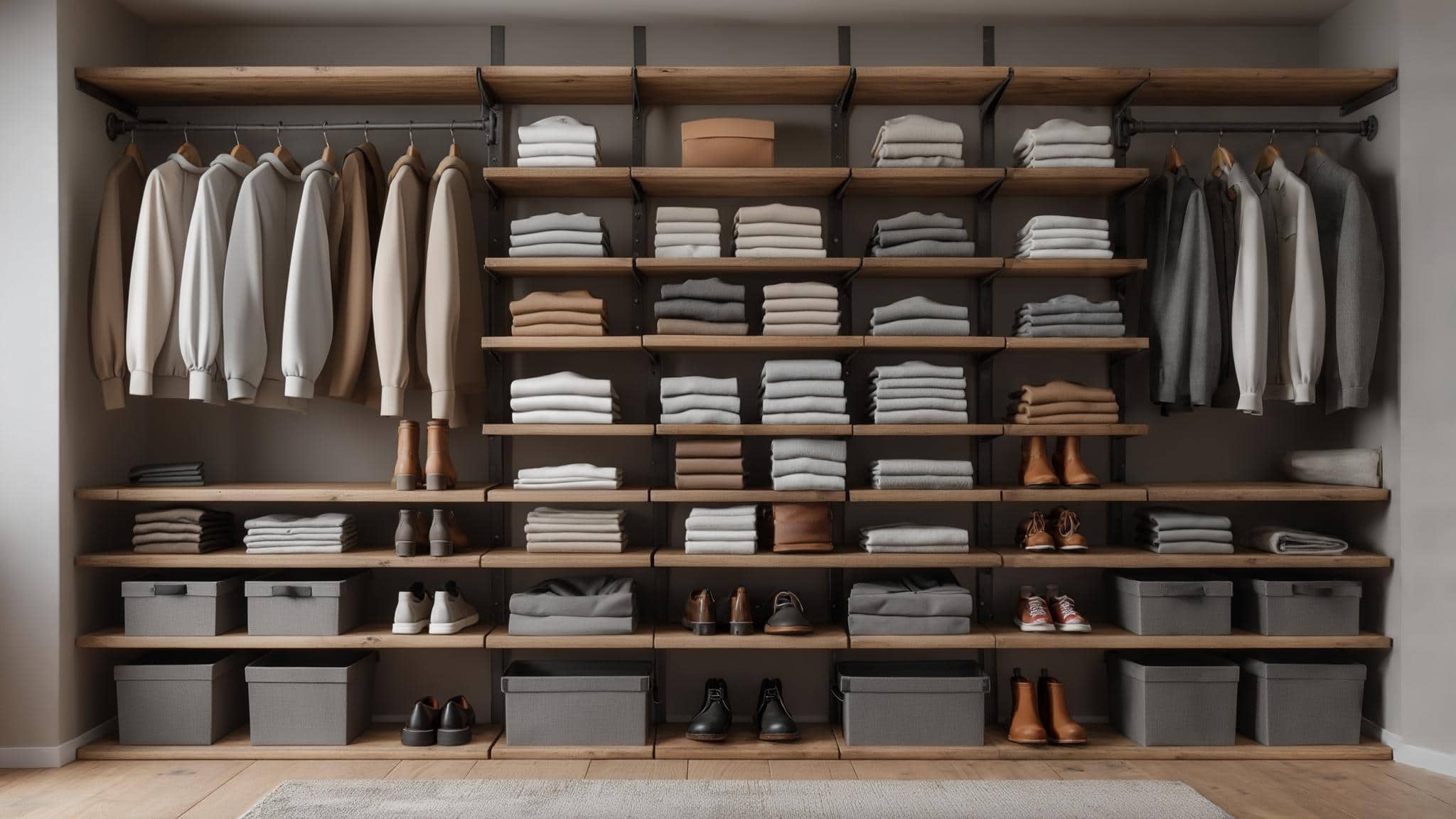
A closet with 15 different categories of hanging space (work shirts, casual shirts, short sleeves, long sleeves, etc.) forces your brain to process multiple decisions for a single item. Instead, create three clear zones: daily wear (power zone), occasional wear, and seasonal storage. This reduces decision time from 15+ seconds to under 3 seconds per item.
Visual Weight and Natural Item Migration
Items with darker colors and bulkier shapes create the perception of heaviness that influences where people naturally want to place them. Understanding this psychological tendency helps you design shelf layouts that work with human instincts rather than against them.
Dark-colored clothing appears heavier to the brain and naturally migrates to lower shelves over time. Bulky items like sweaters and coats create visual weight that affects the perceived balance of your entire closet system.
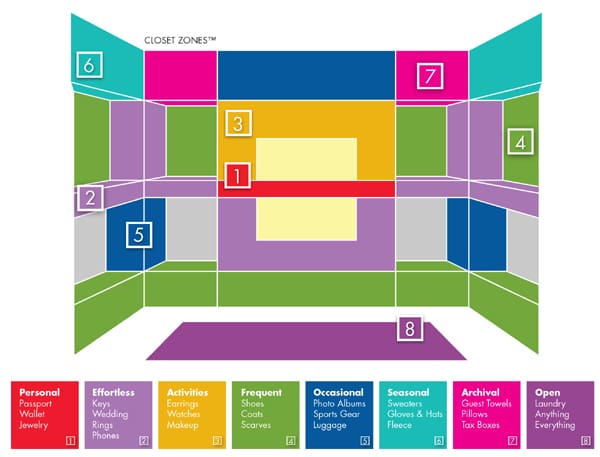
Creating Psychological Territories in Your Closet
Professional organizers succeed by creating distinct psychological zones for different life contexts within closet spaces. Each shelf area should serve a specific behavioral purpose, with clear boundaries that prevent the mixing of different item categories.
Micro-zones reduce decision fatigue by creating obvious homes for specific item types. The power zone principle places daily-use items in the 24-48 inch height range where you can reach without stretching or bending. Seasonal transition mapping builds flexibility into your system for the psychological shift between storing different types of clothing.
|
Zone Type |
Height Range |
Best For |
Access Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Power Zone |
24-48 inches |
Daily essentials, work clothes |
Multiple times daily |
|
Upper Storage |
48-72 inches |
Seasonal items, rarely used |
Weekly/monthly |
|
Lower Storage |
0-24 inches |
Shoes, heavy items, storage bins |
Daily to weekly |
|
Top Shelf |
72+ inches |
Long-term storage, out-of-season |
Seasonal only |
The Power Zone for Daily Essentials
Items you use daily should occupy the 24-48 inch height range, which represents your natural reach without stretching or bending. This power zone becomes the most valuable real estate in your closet and determines how smoothly your morning routine flows.
The power zone aligns with natural arm movement patterns and reduces physical strain during daily use. Items placed outside this zone get used less frequently, regardless of how much you think you need them.
Planning for Seasonal Storage Transitions
Successful closet systems accommodate the psychological shift between storing winter coats and summer dresses. Design your shelves with built-in flexibility that makes seasonal transitions feel natural rather than overwhelming.
Seasonal transition mapping prevents the twice-yearly closet reorganization crisis that leads many people to abandon their systems. Flexible shelf spacing allows you to adjust storage configurations without reinstalling hardware.
Preventing the Forgotten Middle Syndrome
The middle shelf in any three-shelf system becomes a catch-all unless you specifically design constraints to prevent this behavior. Understanding this tendency helps you create purposeful limitations that maintain organization.
Middle shelves lack the visual prominence of top shelves and the convenience of bottom shelves, making them prone to becoming dumping grounds. Physical constraints like dividers or specific-sized containers prevent the gradual accumulation of miscellaneous items.
Engineering Behavioral Triggers Into Your Design
Every shelf placement either encourages good organizational habits or enables clutter accumulation through unconscious behavioral cues. Strategic design creates commitment devices that make maintaining your system easier than abandoning it.
Behavioral trigger engineering uses physical design elements to prompt desired actions automatically. Commitment device strategies create physical constraints that make it harder to abandon your organization system than to maintain it. Unconscious behavioral cues influence daily habits more than conscious decision-making about organization.
Understanding Load Distribution and Material Science
Most DIY closet shelves failures result from misunderstanding how weight travels through your closet system over time, not from poor construction techniques. Your shelves absorb cumulative stress from thousands of daily loading and unloading cycles, while materials respond to sustained weight in ways that affect long-term performance and appearance.
Understanding the physics behind your project becomes even more critical when you’re dealing with heavy furniture removal during renovation phases, as improper load calculations can lead to both structural damage and safety hazards during the construction process.
Dynamic loading from daily use creates different stress patterns than static weight calculations suggest. Material memory and creep cause different shelf materials to respond uniquely to sustained loading over months and years. Cascading failure principles mean that when one component begins to fail, it redistributes stress to other parts in predictable patterns.
Dynamic vs. Static Loading Realities
Your DIY closet shelves don’t just hold weight – they absorb the cumulative impact of thousands of micro-impacts from daily use. A shelf that can hold 50 pounds when loaded once might fail at 30 pounds after six months of daily loading and unloading cycles.
The fatigue multiplier effect reduces actual weight capacity significantly below theoretical static load limits. Resonance frequency considerations matter because closet doors create air pressure changes that cause shelves to vibrate at specific frequencies. Daily loading cycles create stress patterns that differ dramatically from one-time weight tests.
The Fatigue Multiplier Effect on Weight Capacity
Repeated loading and unloading cycles reduce your shelf’s effective weight capacity through accumulated micro-damage that isn’t visible until failure occurs. This fatigue multiplier effect explains why shelves that seem sturdy initially can fail unexpectedly after months of normal use.
Micro-fractures accumulate in materials with each loading cycle, eventually reaching critical failure points. The difference between static and dynamic load capacity can be 30-40% for common DIY materials.
Based on real-world testing, “the total cost for this eight foot wide closet storage system was $278” according to DIY Pete, demonstrating that proper load distribution planning can create durable systems at a fraction of commercial alternatives.
Vibration and Resonance From Daily Door Movement
Closet doors create air pressure changes that cause shelves to vibrate at specific frequencies, leading to gradual fastener loosening over time. This often-overlooked factor contributes to many seemingly mysterious shelf failures.
Air pressure changes from door opening and closing create consistent vibration patterns that affect fastener integrity. Resonance frequencies vary based on shelf length and mounting method, requiring different mitigation strategies.
How Materials Change Under Sustained Weight
Different materials respond to sustained loading through compression, expansion, and structural changes that affect both performance and appearance over time. Understanding material memory and creep helps you choose appropriate materials and plan for long-term maintenance needs when building how to make closet shelves DIY projects.
Wood fiber compression rates vary significantly between particle board (3-5% compression in year one) and solid wood (less than 1% compression). Metal bracket stress concentration creates failure points that weaken over time, especially when overloaded by just 10-15%. Composite material expansion cycles from temperature and humidity changes create micro-movements that compound over time.
Wood Compression and Expansion Patterns
Particle board compresses 3-5% over the first year under constant load, while solid wood compresses less than 1%. These different compression rates affect shelf levelness and load distribution as your system ages.
Different wood products respond uniquely to sustained loading, affecting long-term shelf performance and appearance. Compression rates accelerate in high-humidity environments, making material selection crucial for closet applications.
Metal Bracket Stress Points and Failure Modes
Standard L-brackets create stress concentration points that weaken over time, especially when overloaded by just 10-15% above their rated capacity. Understanding these failure modes helps you select appropriate hardware and installation methods.
Stress concentration occurs at bracket corners and mounting points, creating predictable failure patterns. Overloading by small amounts (10-15%) causes gradual weakening that leads to sudden failure rather than obvious warning signs.
Preventing Cascading System Failures
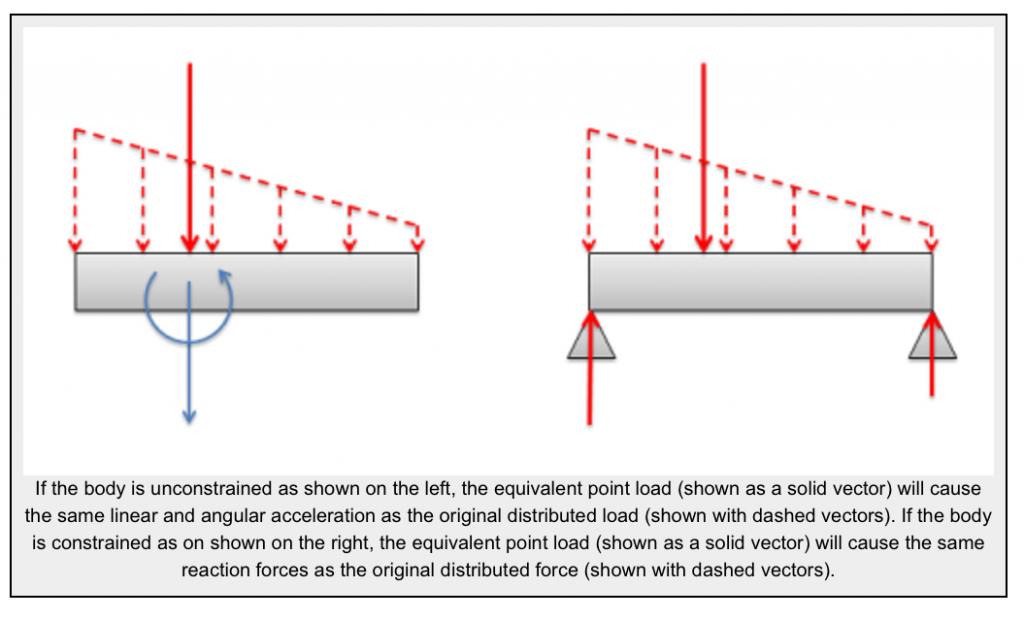
When one shelf component begins to fail, it redistributes stress to other components in predictable patterns that can cause your entire system to collapse. Understanding load path analysis and implementing early warning detection prevents catastrophic failures.
Load path analysis shows how weight transfers from shelf to bracket to wall stud, revealing potential failure points. Early warning detection systems use simple visual indicators to alert you to developing problems before they become expensive disasters. Cascading failure prevention requires understanding how component failures affect the entire system’s stability.
Strategic Installation Planning for Long-Term Success
Professional contractors think in decades, not weekends, transforming DIY closet shelves projects from temporary fixes into permanent assets. This approach requires understanding what’s hidden behind your closet walls, planning for future modifications, and designing systems that can be removed without damage if needed.
Before beginning any major closet renovation, consider how your project might generate waste that requires professional decluttering services to handle efficiently, especially when dealing with old shelving systems and accumulated storage items.
Pre-installation archaeology reveals hidden information in your closet walls that determines project success or failure. The reversibility principle plans installations as if you’ll need perfect removal in five years without wall damage. Future-proofing integration points accommodate technologies and storage needs that don’t exist yet.
Discovering What’s Hidden Behind Your Walls
Your closet walls contain crucial information about stud quality, previous modifications, and hidden obstacles that electronic stud finders often miss. Understanding electrical and plumbing locations prevents costly mistakes and creates opportunities for integrated solutions.
Stud mapping beyond electronic finders reveals stud quality, previous modifications, and hidden obstacles that affect installation success. Electrical and plumbing forensics prevent costly mistakes while identifying opportunities for integrated lighting or power solutions. Load-bearing assessment techniques determine which walls can handle heavy shelving systems versus those requiring special considerations.
Advanced Stud Detection and Quality Assessment
Electronic stud finders miss crucial details about stud quality, previous modifications, and hidden obstacles that can derail your installation. Advanced detection techniques reveal the true condition of your wall structure before you commit to specific mounting locations for your how to make closet shelves DIY project.
Stud quality varies significantly even within the same wall, affecting holding power for heavy shelf systems. Previous modifications like electrical work or plumbing changes can compromise stud integrity in ways that electronic finders don’t detect.
Electrical and Plumbing Location Mapping
Understanding what’s behind your walls prevents expensive mistakes and creates opportunities for integrated solutions like built-in lighting or power outlets. This forensic approach turns potential obstacles into design advantages.
Electrical and plumbing locations often follow predictable patterns that you can map without opening walls. Hidden utilities can become integration opportunities rather than obstacles when identified during planning phases.
Planning for Future Modifications and Removal
The reversibility principle plans your installation as if you’ll need to remove it perfectly in five years without damaging the closet. This approach uses modular connection systems and wall preservation strategies that maintain flexibility while maximizing holding power.
Modular connection systems allow disassembly and reconfiguration as needs change without starting over. Wall preservation strategies minimize permanent modifications while maximizing holding power through strategic fastener selection. Documentation for future modifications helps future you or the next homeowner understand and modify your system.
Modular Design for Easy Reconfiguration
Building your DIY closet shelves system in components that can be installed, adjusted, and replaced independently provides long-term flexibility. Modular connections work with multiple shelf types and configurations, preventing obsolescence as your needs change.
Universal interface concepts create connections that work with multiple shelf types and future modifications. Staged installation approaches let you test functionality before committing to the complete design.
Minimizing Permanent Wall Modifications
Strategic fastener selection and mounting techniques maximize holding power while minimizing permanent wall damage. This approach maintains structural integrity while preserving your ability to modify or remove the system cleanly.
Wall preservation strategies balance holding power with reversibility, using techniques that distribute load without creating permanent damage. Strategic fastener selection considers both immediate holding power and long-term removal requirements.
Accommodating Unknown Future Needs
Future-proofing integration points design your shelving system to accommodate technologies and storage needs that don’t exist yet. This includes planning conduit paths for smart home integration and designing flexibility for changing physical capabilities over time.
Smart home preparation plans conduit paths and power access for future lighting, sensors, or automated systems. Accessibility evolution planning designs flexibility for changing physical capabilities as you age. Technology integration points accommodate future innovations without requiring system redesign.
Simple Construction Methods That Outperform Complex Designs
The most successful easy DIY closet shelves use counterintuitive approaches that prioritize function over appearance while achieving both. Constraint-based design methods and modular assembly strategies create systems that are easier to build, adjust, and maintain than elaborate alternatives.
When planning your construction approach, remember that garage cleanout services can help clear workspace for your project, providing the organized environment necessary for precise construction work.
The constraint-based design method produces better results by working within limitations rather than pursuing unlimited options. The three-material rule forces creative solutions while reducing decision paralysis during construction. Modular assembly strategies build systems in components that can be installed, adjusted, and replaced independently.
Working Within Smart Limitations
Constraints force creative solutions and prevent decision paralysis that derails many DIY projects. Limiting yourself to three materials creates focus while ensuring compatibility between components throughout your system.
Decision paralysis increases exponentially with available options – artificial constraints improve both decision speed and final results. Material compatibility issues decrease dramatically when you limit your component palette to three complementary options. Creative problem-solving emerges naturally when you must work within defined boundaries rather than having unlimited choices.
The Three-Material Rule for Better Results
Restricting your project to three materials eliminates compatibility issues while forcing innovative solutions. This constraint prevents the common DIY mistake of mixing incompatible materials that create weak points or aesthetic problems in how to make closet shelves DIY projects.
Three-material systems ensure thermal expansion compatibility and consistent aging patterns across all components. Limited material palettes create visual cohesion automatically without requiring advanced design skills.
Real-world projects demonstrate this principle’s effectiveness, as “we estimate we spent around $380 for building materials” according to Deeply Southern Home, proving that constraint-based approaches deliver professional results while controlling costs.
Building in Manageable Components
Modular assembly breaks your project into manageable pieces that can be tested individually before final installation. Universal interface concepts and staged installation approaches reduce risk while maintaining flexibility for future adjustments.
Component-based construction allows you to perfect each piece before assembly, reducing waste and rework. Universal interfaces create connection points that accommodate multiple shelf configurations and future modifications. Staged installation lets you verify functionality at each phase before committing resources to the next step.
“While some individuals might have goals and budgets that allow them to entertain the idea of a fully personalized, designer closet, this reality is out of reach for the vast majority of people” according to House Digest, emphasizing why modular, component-based approaches provide accessible solutions for custom storage needs.
Creating Universal Connection Points
Designing connections that work with multiple shelf types prevents obsolescence and enables easy modifications. These universal interfaces become the foundation for a system that can evolve with changing needs.
Universal connection standards eliminate the need to rebuild entire systems when making modifications. Interface compatibility extends the useful life of your investment by accommodating future component upgrades.
Testing Before Full Commitment
Staged installation approaches install your simple DIY closet shelves system in phases to test functionality before committing to the complete design. This method identifies problems when they’re still easy and inexpensive to fix.
Phase-based installation reveals design flaws and usage pattern mismatches before they become expensive problems. Functionality testing with temporary installations validates your design assumptions using real-world conditions.
Build and temporarily install one complete shelf section first. Live with it for a week, noting how you actually use the space versus how you planned to use it. If you find yourself constantly reaching for items on the “seasonal” shelf, adjust your design before building the remaining sections. This one-week test can prevent months of frustration with a poorly planned system.
Managing Precision in Real-World Conditions
The invisible tolerance stack compounds small measurement errors across your entire system. Managing cumulative errors, temperature coefficients, and settling accommodation prevents the visible problems that make DIY projects look amateur.
Cumulative error management prevents small individual mistakes from creating large system-wide problems. Temperature coefficient planning accounts for different expansion rates between materials like metal brackets and wood shelves. Settling accommodation strategies handle the reality that buildings move and change over time.
Preventing Error Accumulation
A 1/16″ error across six shelf positions creates a 3/8″ deviation that makes your top shelf visibly crooked. Understanding how small errors compound helps you build precision into your process rather than hoping for perfection.
Error accumulation follows predictable mathematical patterns that you can plan for and prevent. Measurement precision becomes more critical as system size increases due to cumulative effects.
Accounting for Material Movement
Different materials expand at different rates, creating seasonal fit issues between metal brackets and wood shelves. Planning for these movements prevents binding, warping, and connection failures.
Thermal expansion coefficients vary significantly between common DIY materials, requiring accommodation in connection design. Seasonal movement patterns are predictable and can be designed around rather than ignored.
Anti-Sag Engineering Without Complexity
Preventing shelf bow requires understanding beam theory principles rather than simply adding more brackets. The golden ratio of support placement and edge-loading resistance create stronger shelves with fewer components.
The 1/3 rule places supports at optimal points for maximum strength with minimum hardware. Edge-loading resistance accounts for the reality that items naturally migrate toward shelf edges over time. Beam theory principles apply to DIY construction and dramatically improve performance when understood.
Optimal Support Placement
The golden ratio of support follows the 1/3 rule: place supports at 1/3 and 2/3 points along shelf length for maximum strength. This placement outperforms evenly spaced brackets or supports placed only at the ends.
Mathematical optimization of support placement reduces material requirements while increasing load capacity. The 1/3 rule works across different shelf lengths and materials, providing a universal design principle.
Designing for Natural Item Migration
Items naturally migrate toward shelf edges over time due to daily use patterns and gravity effects. Designing for this reality rather than fighting it creates more durable and functional storage systems.
Edge-loading patterns are predictable based on item types and usage frequency, allowing proactive design solutions. Resistance strategies work with natural forces rather than attempting to prevent inevitable item movement.
Installation Sequencing to Avoid Costly Mistakes
The accessibility cascade method installs components in an order that maintains access to adjustment points throughout the process. Top-down installation strategies and built-in quality control checkpoints prevent the need to redo completed work when problems emerge.
Proper installation sequencing becomes even more critical when you’re working around existing items that may require furniture removal or donation decisions during the construction process, as timing these removals incorrectly can create workspace constraints.
The accessibility cascade method maintains access to critical adjustment points throughout the installation process. Top-down versus bottom-up strategies each offer specific advantages depending on your closet configuration and tool access. Quality control checkpoints built into the installation sequence catch problems before they require expensive rework.
Maintaining Access Throughout Installation
Installing components in the wrong order can trap you in corners or block access to critical fasteners, forcing you to partially disassemble completed work. Strategic sequencing prevents these accessibility problems in your DIY closet shelves project.
Tool access preservation plans your installation sequence to avoid blocking critical work areas or fastener locations. Component accessibility affects both installation efficiency and future maintenance requirements. Installation sequence impacts both immediate construction success and long-term system serviceability.
Top-Down Installation Advantages
Starting from the top shelf down prevents debris from falling on completed work and allows for easier leveling adjustments. This approach also maintains better access to upper mounting points throughout the process.
Debris management becomes automatic when working from top to bottom, protecting finished surfaces. Leveling adjustments are easier when you can reference completed upper shelves for alignment.
Preserving Critical Access Points
Planning your installation sequence to avoid trapping yourself in corners or blocking access to critical fasteners prevents frustrating rework. This forward-thinking approach saves time and reduces installation stress.
Critical fastener access must be maintained throughout installation to allow for adjustments and corrections. Corner entrapment occurs when installation sequence blocks your ability to reach remaining work areas.
Building Quality Control Into Your Process
The 5-point verification system checks level, plumb, square, spacing, and load capacity at each stage before proceeding. Stress test protocols and aesthetic alignment confirmation catch problems while changes are still simple to make.
The 5-point verification system creates systematic checkpoints that prevent small problems from becoming major issues. Stress test protocols gradually load shelves with temporary weight to identify weak points before permanent installation. Aesthetic alignment confirmation requires stepping back frequently to assess visual balance during construction.
|
Checkpoint |
What to Verify |
Tools Needed |
Acceptable Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Level |
Horizontal surfaces |
2-foot level |
±1/8″ over 4 feet |
|
Plumb |
Vertical alignment |
4-foot level |
±1/8″ over 8 feet |
|
Square |
90-degree corners |
Speed square |
±1/16″ diagonal difference |
|
Spacing |
Consistent gaps |
Measuring tape |
±1/16″ between components |
|
Load |
Weight capacity |
Test weights |
No visible deflection |
Systematic Verification at Each Stage
Checking level, plumb, square, spacing, and load capacity at each installation stage prevents cumulative errors that become expensive to fix later. This systematic approach catches problems when corrections are still straightforward.
Five-point verification creates a repeatable quality control process that works regardless of skill level. Stage-based verification prevents error accumulation that can compromise the entire system.
Load Testing Before Final Installation
Gradually loading shelves with temporary weight identifies weak points before you commit to permanent installation. This testing reveals problems that aren’t apparent during unloaded assembly of how to make closet shelves DIY systems.
Temporary load testing simulates real-world conditions without the risk of permanent damage. Weak point identification during testing prevents failures that could damage stored items or surrounding walls.
Planning for Common Problems
Every installation should include predetermined solutions for common problems. The adjustment buffer zone and camouflage strategies provide recovery options when minor imperfections occur despite careful planning.
Recovery planning anticipates common installation problems and prepares solutions before they’re needed. The adjustment buffer zone builds 1/4″ of fine-tuning capability into each connection point. Camouflage strategies hide small imperfections using trim, paint, or strategic item placement.
Building in Adjustment Capability
Building 1/4″ of adjustment capability into each connection point provides fine-tuning options that accommodate real-world installation conditions. This buffer zone prevents minor measurement errors from becoming visible problems.
Adjustment buffers accommodate the reality that real-world conditions never match perfect measurements. Fine-tuning capability built into connections allows for corrections without hardware replacement.
Hiding Minor Imperfections
Planning how to hide small imperfections using trim, paint, or strategic item placement provides backup options when perfection isn’t achievable. These camouflage strategies maintain professional appearance despite minor flaws.
Camouflage planning prepares aesthetic solutions for common imperfections before they occur. Strategic concealment techniques can make minor flaws invisible without major rework.
If your top shelf ends up 1/8″ higher on the right side despite careful measurement, install a decorative trim piece along the ceiling line. The trim creates a visual reference that makes the shelf appear level while hiding the actual deviation. This camouflage costs $15 in materials versus $200+ to rebuild the entire upper section.
Predicting and Preventing Future Maintenance Issues
Different shelf areas experience different types of stress based on usage patterns and item types. Understanding wear pattern analysis and material fatigue scheduling helps you plan maintenance based on expected wear rates rather than waiting for failures to occur.
Understanding maintenance patterns becomes especially important when your project generates debris that requires professional debris removal services during periodic maintenance and upgrade cycles.
Wear pattern analysis identifies which shelf areas will experience different stress types based on usage patterns and stored item characteristics. Material fatigue scheduling plans component replacement based on expected wear rates rather than reactive failure response. Preventive intervention points identify specific maintenance tasks that prevent major problems when performed regularly.
Understanding How Different Areas Wear Out
High-traffic zones require different engineering approaches than seasonal storage areas. Analyzing usage patterns helps you reinforce areas that will experience heavy use while avoiding over-engineering areas that see minimal stress in your DIY closet shelves system.
High-traffic zone reinforcement focuses engineering resources where they’ll have the greatest impact on system longevity. Usage pattern analysis reveals which areas need robust construction versus those where standard approaches suffice. Stress type variation across different shelf areas requires targeted maintenance approaches rather than uniform treatment.
Reinforcing High-Use Areas
Areas accessed daily require different engineering approaches than seasonal storage zones. Understanding these usage patterns helps you allocate reinforcement where it will have the greatest impact on system longevity.
Daily access areas experience different stress patterns than occasional-use zones, requiring targeted reinforcement strategies. Engineering resource allocation becomes more effective when based on actual usage patterns rather than uniform approaches.
Professional organizers recognize that “I’m pretty short, only 5’1″” according to Deeply Southern Home, emphasizing how individual usage patterns and physical characteristics should determine reinforcement priorities in high-use areas.
Scheduling Component Replacement
Planning replacement schedules for components based on expected wear rates prevents sudden failures that can damage stored items or surrounding structures. This proactive approach costs less than reactive repairs.
Proactive replacement scheduling prevents failures that could damage valuable stored items or require emergency repairs. Expected wear rates vary significantly between different components and usage patterns, requiring individualized maintenance schedules.
Implementing Preventive Maintenance Systems
Fastener tension monitoring and surface protection renewal represent specific maintenance tasks that prevent major problems when performed regularly. These interventions cost minimal time and money while preventing expensive failures in your easy DIY closet shelves system.
Fastener tension monitoring prevents gradual loosening from vibration and thermal cycling that leads to sudden failures. Surface protection renewal maintains both functional performance and aesthetic appearance through planned maintenance cycles. Regular preventive interventions cost significantly less than emergency repairs or complete system replacement.
Monitoring Connection Integrity
Checking and re-tightening connections quarterly prevents gradual loosening from vibration and thermal cycling. This simple maintenance task prevents most connection-related failures before they occur.
Quarterly connection checks catch loosening before it progresses to failure, preventing damage to stored items and surrounding structures. Vibration and thermal cycling create predictable loosening patterns that regular maintenance can prevent.
Protecting High-Contact Surfaces
Planning for periodic refinishing of high-contact surfaces maintains both function and appearance over years of use. This scheduled maintenance prevents wear patterns that make systems look shabby and function poorly.
High-contact surface protection prevents wear patterns that compromise both appearance and functionality. Scheduled refinishing costs less than replacement while maintaining system performance and aesthetic appeal.
How Professional Decluttering Services Support Your DIY Success
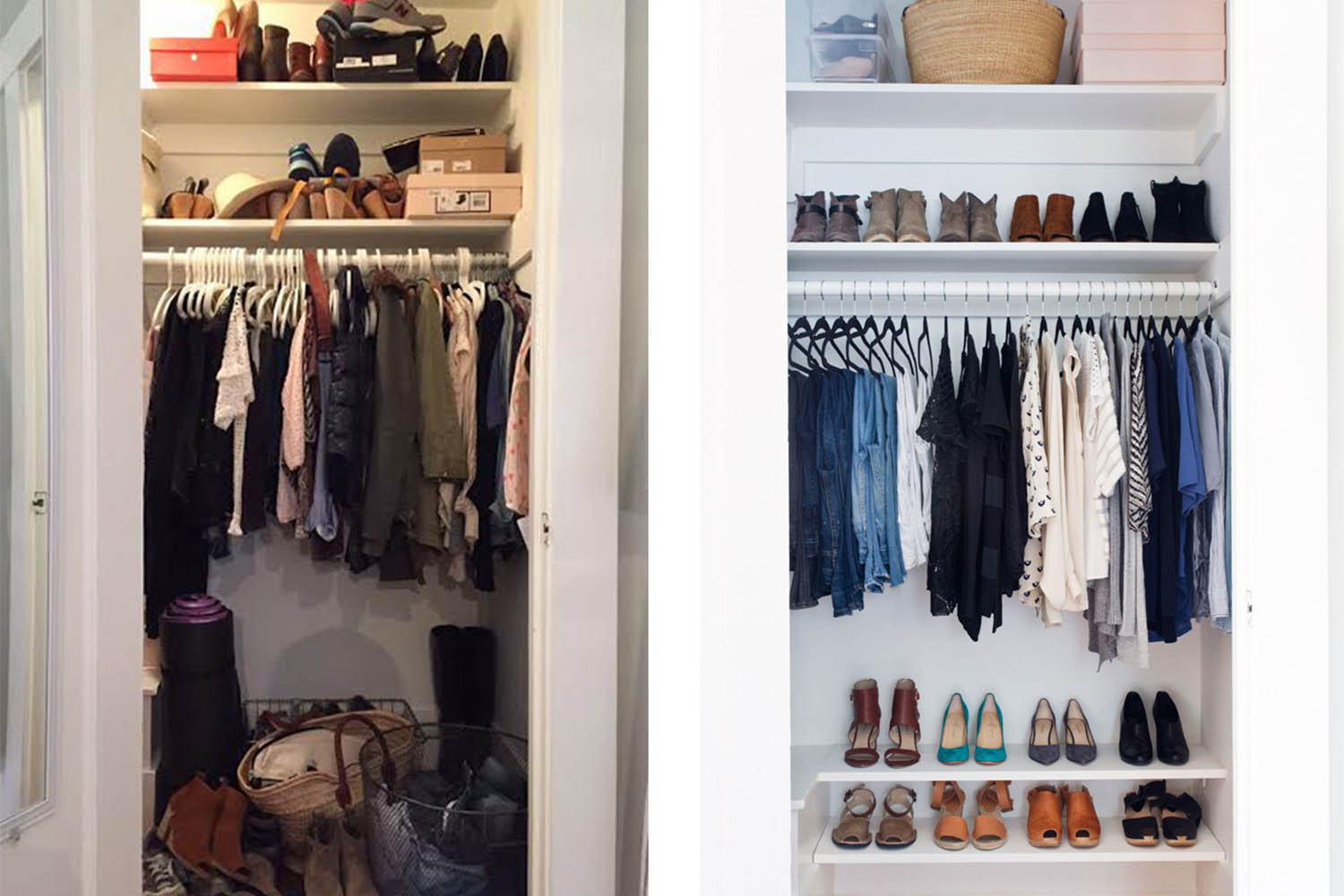
Strategic decluttering before beginning your DIY closet shelf project clarifies what truly deserves space on your new shelves versus what should be removed from your home entirely. Professional services understand the emotional attachment people have to belongings and can help make decisions that support long-term organization goals while ensuring removed items find appropriate second lives through donation or recycling.
Professional decluttering services work hand-in-hand with your construction timeline, especially when coordinating estate cleanout services that may be necessary before beginning major closet renovations in inherited or purchased homes.
Pre-construction decluttering clarifies storage requirements and prevents building shelves for items you don’t actually need to keep. Professional sorting expertise helps identify which items deserve prime real estate in your new system versus those taking up space due to decision avoidance. Eco-friendly removal ensures items find appropriate second lives rather than simply shifting clutter problems to landfills.
Jiffy Junk’s “White Glove Treatment” approach transforms overwhelming closet preparation into manageable decision-making. Their team’s experience with residential cleanouts means they understand the psychology behind keeping items you don’t use while helping you focus on what actually supports your daily routines.
The behavioral trigger engineering phase of your project becomes much clearer when you’re not trying to organize around items you don’t actually need. Professional decluttering services can be especially valuable during this phase, helping you identify which belongings actually deserve the prime real estate in your power zone versus those that are simply occupying space due to decision avoidance.
Ready to start your DIY closet shelf project with a clean slate? Contact Jiffy Junk today to schedule your pre-construction decluttering consultation and transform your closet preparation from overwhelming to manageable.
Final Thoughts
Building DIY closet shelves that last requires understanding the hidden psychology and physics that most people overlook. Your success depends less on carpentry skills and more on designing systems that work with human behavior patterns and material science principles.
The most important insight from this comprehensive approach is that professional-quality results come from thinking in decades rather than weekends. When you plan for behavioral patterns, material fatigue, and future modifications from the beginning, your DIY project becomes a permanent asset rather than a temporary fix.
Remember that every shelf placement either encourages good habits or enables clutter accumulation. The physics of load distribution, the psychology of decision-making, and the reality of material behavior all work together to determine whether your system thrives or fails over time.
Long-term thinking transforms DIY projects from temporary fixes into permanent home improvements that add value and functionality. Understanding behavioral patterns and material science principles matters more than advanced carpentry skills for creating successful storage systems. Integration of psychological design, proper engineering, and strategic planning creates closet systems that improve rather than complicate daily routines.