DIY Garage Psychology: The Hidden Mental Game That Makes or Breaks Your Automotive Projects
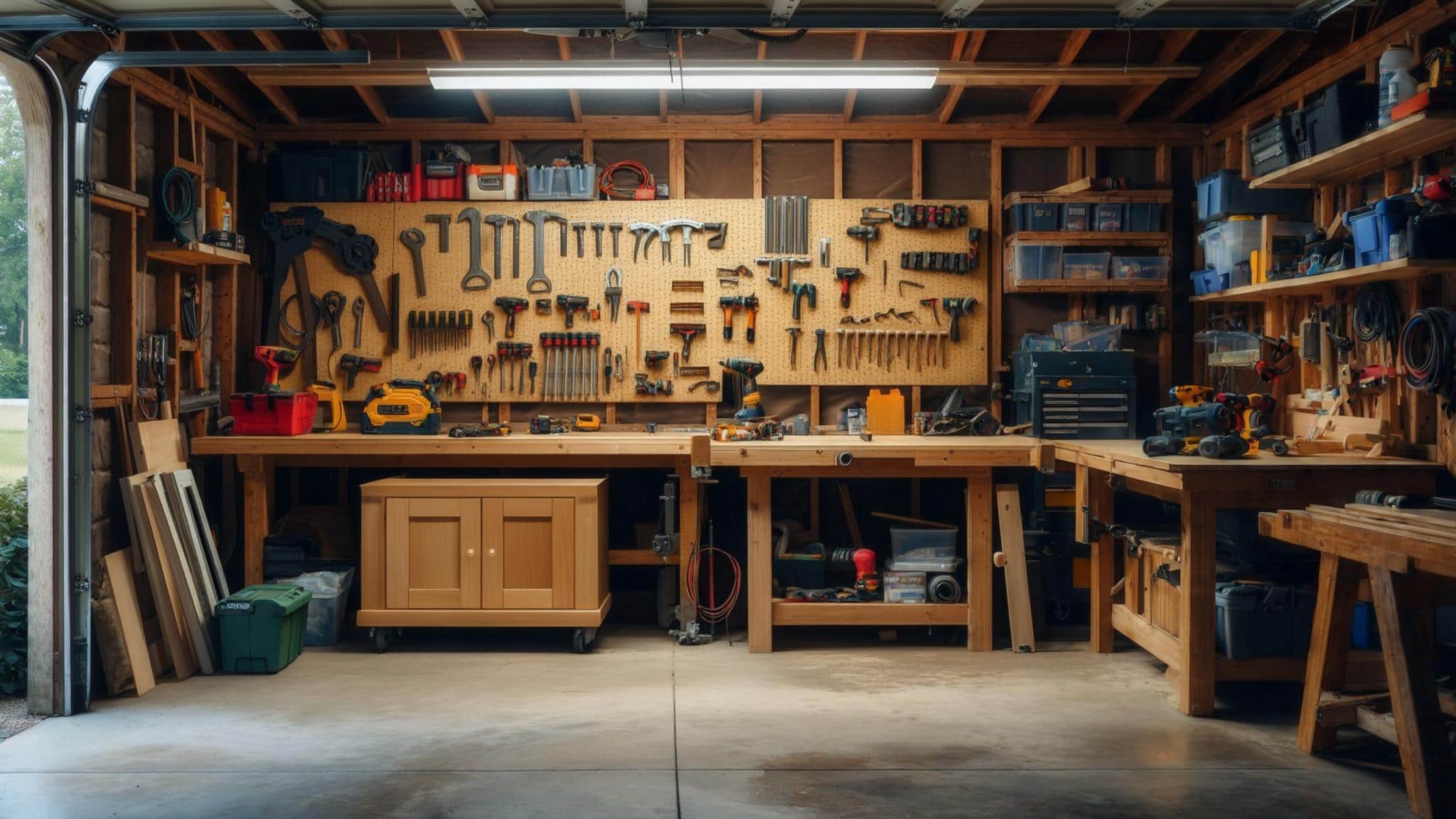
Your garage represents far more than just a parking space for most homeowners – it’s a multifunctional environment where psychology, organization, and automotive expertise intersect. Research shows that “only 11% of homeowners are satisfied with their garage organization”, highlighting the widespread challenge of creating functional automotive workspaces that support both mental clarity and technical precision.
The Psychological Architecture of DIY Automotive Spaces
Most diy garage discussions focus on tools and techniques, but the real foundation lies in understanding how your physical workspace shapes your mental state, decision-making abilities, and long-term project success. The psychology of your workspace directly impacts your ability to learn new skills, retain complex information, and complete challenging automotive tasks without frustration or errors.
Scientific research shows that cluttered environments increase stress hormones and reduce your brain’s processing power by nearly one-third, which becomes critical when working on precision automotive tasks that require sustained focus and attention to detail. Your workspace psychology creates either a foundation for success or a barrier to achievement, making the difference between projects that flow smoothly and those that become sources of ongoing frustration and incomplete work.
The foundation of any successful diy garage begins with understanding how to properly clean your garage space before implementing psychological optimization strategies.
The Neuroscience of Organized Workspaces
Scientific research reveals that cluttered environments increase cortisol levels and reduce cognitive performance by up to 32%. In automotive work, where precision and safety are paramount, your brain’s ability to process information directly correlates with how well you organize your physical space. This connection between environment and mental performance becomes the foundation for everything else you’ll accomplish in your diy garage.
Cortisol elevation from disorganized spaces doesn’t just affect your mood – it actively impairs your working memory, making it harder to follow complex repair procedures or remember the sequence of steps you’ve already completed. Your brain processes spatial information before it can focus on technical tasks, so every moment spent searching for tools or navigating clutter is cognitive energy that could be directed toward solving mechanical problems.
Professional mechanics unconsciously create organized systems because their livelihood depends on efficiency, but DIY enthusiasts can achieve the same cognitive benefits by understanding and implementing these same organizational principles. According to Webfoot Home research, homeowners open their garage doors approximately 1,500 times per year, meaning your organizational system (or lack thereof) impacts your mental state and productivity over 1,000 times annually.
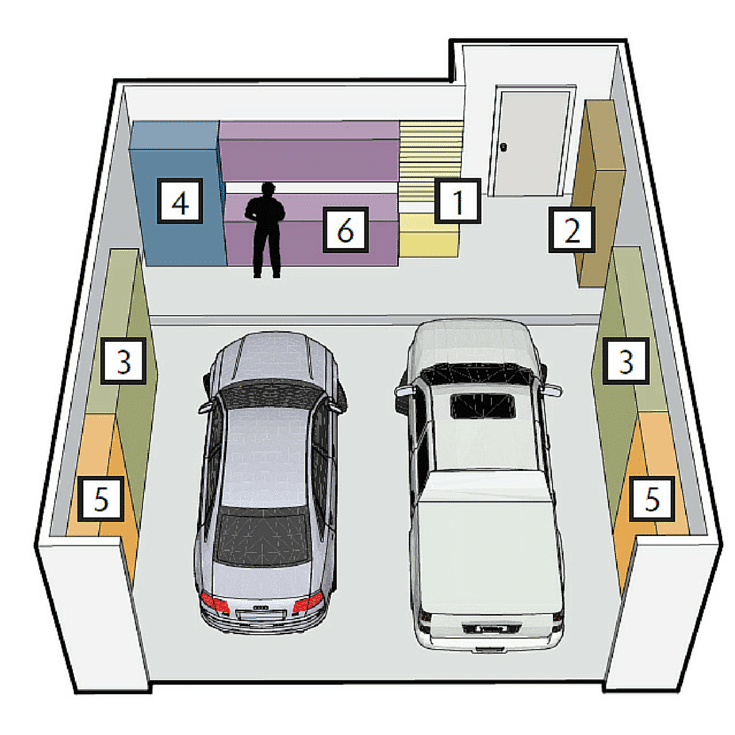
The 5-Zone Cognitive Mapping System
Professional mechanics unconsciously organize their workspace into five distinct cognitive zones that mirror how the brain processes sequential tasks. Understanding and implementing this system can reduce your project time by 40% and significantly decrease errors. These zones work with your natural movement patterns and mental processing to create an environment where complex tasks feel more manageable.
Your brain naturally categorizes tasks by frequency and complexity, so organizing your physical space to match these mental categories reduces the cognitive load of decision-making during projects. Movement patterns during automotive work follow predictable sequences based on task progression, and aligning your tool placement with these patterns eliminates wasted motion and mental energy.
Visual boundaries created through floor tape or lighting help your brain maintain spatial awareness without conscious effort, allowing more mental resources to focus on the technical aspects of your work. Testing and adjusting zones based on actual workflow data ensures your system evolves with your skills and project types rather than remaining static and potentially counterproductive.
When planning your diy garage zones, consider starting with professional garage clean-out services to create the blank canvas needed for optimal zone implementation.
|
Zone |
Purpose |
Tools/Equipment |
Cognitive Function |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Primary Work |
Active project focus |
Current project tools, work surface |
High concentration tasks |
|
Secondary Access |
Frequently used items |
Common tools, consumables |
Quick retrieval without thought |
|
Storage Buffer |
Project-specific items |
Specialty tools, parts |
Organized staging area |
|
Reference Zone |
Information and documentation |
Manuals, computer, measurement tools |
Knowledge access and verification |
|
Maintenance Area |
Tool care and preparation |
Cleaning supplies, charging stations |
System maintenance and preparation |
Environmental Triggers for Flow State
Flow state – the psychological condition where time seems to stop and complex tasks become effortless – can be artificially triggered through specific environmental modifications that most DIY enthusiasts never consider. Creating the right environmental conditions allows you to access peak performance states consistently rather than hoping they happen randomly.
Lighting systems that adjust between 2700K and 5000K work with your circadian rhythms to maintain alertness during detailed work while preventing eye strain that breaks concentration. Ambient noise levels between 45-55 decibels provide enough background sound to mask distracting noises without overwhelming your ability to hear subtle mechanical sounds that indicate problems or proper function.
Temperature control between 68-72°F keeps your body comfortable without requiring conscious attention, while strategic mirror placement eliminates the need for awkward positioning that creates physical tension and mental distraction. Scent anchoring uses your brain’s powerful connection between smell and memory to create psychological associations with successful work sessions, making it easier to enter focused states.
A DIY enthusiast working on engine rebuilds discovered that playing consistent background music at 50 decibels while maintaining 70°F temperature allowed him to enter flow state within 15 minutes of starting work, reducing his average rebuild time from 12 hours to 8 hours while improving assembly quality.
The Completion Psychology Framework
Unfinished automotive projects create a psychological burden called the “Zeigarnik Effect,” where incomplete tasks consume mental energy even when you’re not actively working on them. Strategic project staging can eliminate this mental drain and help you maintain motivation across long-term builds. Understanding this psychological principle helps you structure projects for success rather than frustration.
Incomplete projects create persistent mental background noise that reduces your ability to focus on current tasks, making each new project feel more overwhelming than it actually is. Strategic staging breaks large projects into psychologically complete phases, allowing your brain to experience satisfaction and closure even when the overall project continues. Documentation of project stages creates external memory storage that reduces the mental energy required to track progress and next steps, freeing cognitive resources for problem-solving and skill development.
Project Completion Checklist:
-
Define clear project phases with measurable endpoints
-
Document completion criteria for each phase
-
Create visual progress tracking system
-
Establish reward system for phase completion
-
Schedule regular project review sessions
-
Plan storage for completed phase materials
The Social Economics of DIY Auto Culture
DIY automotive work exists within a complex social and economic ecosystem that most practitioners don’t fully understand. Mastering these dynamics can transform your hobby into a valuable community asset and potential income stream. The relationships and knowledge networks you build become as valuable as the technical skills you develop.
Every geographic region has informal networks of automotive knowledge sharing that operate outside traditional channels, providing access to expertise and resources unavailable through conventional sources. Understanding the economic principles behind skill monetization helps you make strategic decisions about learning investments and equipment purchases that can eventually pay for themselves. Social dynamics within DIY communities follow predictable patterns that you can leverage to accelerate your learning and build valuable relationships with other enthusiasts and professionals.
Underground Knowledge Networks
Every geographic region has informal networks of automotive knowledge sharing that operate outside traditional channels. Tapping into these networks provides access to rare expertise, specialized tools, and insider information about parts sourcing that can dramatically accelerate your learning and reduce project costs.
These networks often center around specific vehicle platforms, racing communities, or restoration groups where members share specialized knowledge that isn’t available in general automotive resources. Access to these networks typically requires demonstrating genuine interest and willingness to contribute, rather than simply asking for help without offering value in return.
The information shared in these networks often includes insider knowledge about parts interchangeability, supplier relationships, and troubleshooting techniques that can save significant time and money on projects. Recent trends in diy garage organization have gained momentum with spring cleaning initiatives. “DIY Friday with Danielle” from KOB News highlights how proper organization makes future DIY projects significantly easier and more efficient.
The Skill Monetization Ladder
There’s a predictable progression from hobbyist to profitable side business that follows specific economic principles. Understanding this ladder helps you make strategic decisions about skill development and equipment investment. Each level builds on the previous one, creating multiple income streams from your automotive expertise.
Documentation of your learning process creates content value that can be monetized through teaching, writing, or video creation while also reinforcing your own skill development. Developing diagnostic specialties commands higher hourly rates than general repair work because diagnostic skills are harder to develop and more valuable to vehicle owners.
Building referral relationships with local shops creates steady income opportunities while establishing your reputation within the professional automotive community. Teaching and mentoring opportunities generate income and deepen your own understanding while building a network of contacts who may become future customers or collaborators.
The Hidden Infrastructure of Modern DIY Garages
While most garage discussions focus on visible tools and equipment, the real differentiator lies in invisible infrastructure: data systems, supply chains, and technology integration that separate amateur spaces from professional-grade home operations. These systems work behind the scenes to multiply your effectiveness and create compound benefits over time.
Modern diy garage automotive work generates massive amounts of data that most enthusiasts lose due to poor management systems, representing wasted learning opportunities and repeated mistakes. Professional-grade supply chain thinking can reduce project costs by 40-60% while improving quality and availability, but requires systematic approaches that go far beyond buying parts when needed.
Digital Integration and Data Management
Modern DIY automotive work generates massive amounts of data – from diagnostic codes to parts specifications to project timelines. Most enthusiasts lose 30-40% of their accumulated knowledge due to poor data management systems. Creating systematic approaches to information management transforms every project into a learning asset that benefits future work.
Poor data management means you’re constantly relearning information you’ve already discovered, wasting time and mental energy that could be directed toward advancing your skills. Systematic data collection and organization creates institutional memory that compounds over time, making each subsequent project easier and more efficient than the last. Integration with professional diagnostic networks gives DIY enthusiasts access to the same information systems used by dealerships and high-end independent shops, leveling the playing field for complex diagnostics.
The Personal Automotive Database System
Creating a comprehensive personal database system allows you to build institutional memory that compounds over time, turning every project into a learning asset that benefits future work. This system captures what you did, why you did it, and what you learned in the process.
Cloud-based platforms provide accessibility from anywhere while ensuring your data survives equipment failures or location changes, making your knowledge truly portable. Standardized data entry formats ensure consistency that makes information searchable and useful years later, when you might not remember the specific context of a particular project.
Linking systems between projects, parts, and procedures reveal patterns and connections that aren’t obvious during individual projects but become valuable insights over time. Photo and video documentation protocols capture visual information that’s impossible to describe in text, creating reference materials that are immediately useful for similar future problems.
Database Setup Template:
-
Vehicle Information (VIN, year, make, model, modifications)
-
Project Categories (maintenance, repair, modification, diagnostic)
-
Parts Database (part numbers, suppliers, costs, compatibility)
-
Procedure Documentation (step-by-step processes, photos, videos)
-
Troubleshooting Logs (symptoms, diagnosis, solutions, time invested)
-
Cost Tracking (parts, tools, time, total project investment)
Predictive Maintenance Through Personal Analytics
By tracking patterns in your own work and vehicle maintenance, you can develop predictive models that anticipate problems before they occur, dramatically reducing emergency repairs and downtime. Your personal data becomes more valuable than generic maintenance schedules because it reflects your specific vehicles and driving patterns.
Personal maintenance data reveals patterns specific to your vehicles, driving habits, and local conditions that generic schedules can’t account for, leading to more accurate predictions of when components will need attention. Tracking failure patterns across multiple vehicles or years helps identify early warning signs that allow you to address problems during convenient scheduled maintenance rather than emergency roadside situations. Cost analysis of preventive versus reactive maintenance provides concrete data to justify investment in monitoring systems and early intervention strategies.
Integration with Professional Diagnostic Networks
Modern vehicles generate diagnostic data that can be integrated with professional networks, giving DIY enthusiasts access to the same information systems used by dealerships and high-end independent shops. This integration bridges the gap between amateur and professional diagnostic capabilities.
Professional diagnostic networks provide access to technical service bulletins, known issues, and repair procedures that aren’t available through consumer channels, giving you the same information that professional technicians use. Integration with these networks often requires professional-grade diagnostic equipment, but the investment pays for itself through improved diagnostic accuracy and reduced guesswork. Access to manufacturer databases and repair procedures ensures you’re following the same protocols used by factory-trained technicians, improving both safety and effectiveness of your repairs.
Advanced Supply Chain Management
Professional-level DIY operations require sophisticated supply chain thinking that goes far beyond “buying parts when needed.” Strategic sourcing, inventory management, and supplier relationships can reduce project costs by 40-60% while improving quality and availability. This systematic approach transforms parts procurement from a reactive necessity into a strategic advantage.
Different categories of parts require different inventory strategies based on failure predictability, cost, and availability, making a one-size-fits-all approach inefficient and expensive. Building relationships with wholesale suppliers, salvage yards, and specialty manufacturers provides access to parts and pricing unavailable through retail channels, significantly reducing project costs. Understanding parts interchangeability across different vehicle platforms dramatically expands sourcing options and reduces costs, but requires systematic knowledge development that most enthusiasts never pursue.
The Strategic Parts Inventory Matrix
Different categories of parts require different inventory strategies based on failure predictability, cost, and availability. Understanding these categories allows you to optimize cash flow while ensuring project continuity. This systematic approach prevents both overstocking and project delays due to parts unavailability.
Critical high-failure items should be stocked in advance because their failure can strand vehicles or halt projects, making the carrying cost worthwhile compared to the inconvenience and potential emergency pricing of last-minute purchases. Standard maintenance items can be stocked based on usage data and bulk pricing opportunities, balancing inventory costs against the convenience and cost savings of having parts available when needed.
Emergency repair items don’t need to be stocked but require established supplier relationships and documented sources to ensure rapid availability when unexpected failures occur. Specialty and rare items require research and documentation of sources rather than inventory investment, but having this information readily available prevents project delays when these parts are eventually needed.
|
Parts Category |
Inventory Strategy |
Cost Impact |
Availability Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Critical High-Failure |
Stock 2-3 units |
High carrying cost justified |
Immediate availability required |
|
Standard Maintenance |
Bulk purchase on sale cycles |
Medium cost, high savings potential |
1-2 day availability acceptable |
|
Emergency Repair |
Document sources, don’t stock |
Low carrying cost, high urgency premium |
Same-day availability needed |
|
Specialty/Rare |
Research and document only |
Variable, often high unit cost |
Extended lead times acceptable |
|
Consumables |
Bulk stock based on usage |
Low unit cost, high usage frequency |
Always available |
Building Supplier Relationships Beyond Retail
The most successful DIY operations develop relationships with wholesale suppliers, salvage yards, and specialty manufacturers that provide access to parts and pricing unavailable through retail channels. These relationships require investment of time and effort but provide ongoing benefits that compound over years of projects.
Wholesale suppliers often have minimum order requirements or business licensing needs, but the pricing advantages and product availability make the effort worthwhile for serious DIY operations. Salvage yard relationships provide access to rare or discontinued parts at fraction of new costs, but require building trust and demonstrating that you’re a serious customer rather than a casual browser. Specialty manufacturer relationships can provide access to performance parts, custom solutions, or technical support that isn’t available through retail channels, opening up project possibilities that wouldn’t otherwise be feasible.
Cross-Platform Parts Compatibility Systems
Understanding parts interchangeability across different vehicle platforms can dramatically expand your sourcing options and reduce costs, but requires systematic knowledge that most enthusiasts never develop. This knowledge becomes increasingly valuable as vehicles age and original parts become scarce or expensive.
Parts compatibility knowledge allows you to source components from more common or less expensive vehicle platforms while maintaining or even improving performance and reliability. Systematic documentation of successful cross-platform applications creates valuable reference information that saves time and reduces risk on future projects. Understanding the engineering principles behind parts compatibility helps you evaluate potential substitutions safely rather than relying on trial and error or unverified online information.
A DIY enthusiast discovered that brake calipers from a common sedan could be adapted to his classic muscle car restoration, reducing part costs from $800 per caliper to $150 while improving braking performance through modern engineering advances.
The Evolution of DIY Auto Labs
The concept of “DIY auto labs” represents the cutting edge of home automotive work – spaces that blend traditional mechanical work with modern technology, data analysis, and experimental approaches. These environments are designed for learning and innovation, rather than maintenance and repair. They represent the future of serious automotive enthusiasm.
Approaching DIY automotive work with scientific methodology transforms random tinkering into systematic knowledge building, accelerating learning and creating reproducible results that can be shared and validated. Modern diagnostic and measurement tools have become affordable enough for home use, allowing diy garage labs to conduct testing that was previously only possible in professional settings.
Professional scrap metal pick-up services become essential when transitioning your garage into an advanced lab environment, as old equipment and failed experiments can quickly accumulate.
Experimental Design in Automotive Work
Approaching DIY automotive work with scientific methodology transforms random tinkering into systematic knowledge building. This approach accelerates learning and creates reproducible results that can be shared and validated. Scientific methodology prevents expensive mistakes while building genuine expertise that goes beyond following instructions.
Hypothesis-driven approaches allow for controlled testing and measurable results, preventing the expensive trial-and-error cycles that plague random modification attempts. Proper experimental design isolates variables and creates reliable data that can inform future decisions and be shared with other enthusiasts for validation and improvement. Documentation of experimental processes creates valuable intellectual property that can be monetized through teaching, consulting, or content creation while advancing the broader DIY community’s knowledge base.
The Hypothesis-Driven Modification Process
Rather than making random modifications, successful DIY labs use hypothesis-driven approaches that allow for controlled testing and measurable results. This methodology prevents expensive mistakes and builds genuine expertise rather than just accumulated experience. Each modification becomes a learning opportunity that advances your understanding.
Defining specific, measurable objectives before beginning modifications ensures that you’ll be able to determine whether the changes actually achieved their intended goals rather than just assuming they worked. Research of existing data and similar experiments prevents you from repeating mistakes others have already made while building on successful approaches that have been validated.
Single-variable changes allow you to isolate the effects of specific modifications, creating reliable knowledge about what works and why rather than confusion about which of multiple changes produced observed results. Baseline measurements provide objective reference points that eliminate subjective bias and allow accurate assessment of modification effectiveness.
Experimental Modification Protocol:
-
Define specific, measurable hypothesis
-
Research existing data and similar experiments
-
Establish baseline measurements
-
Plan single-variable changes
-
Document all procedures and observations
-
Measure and analyze results
-
Share findings with community for validation
Building Measurement and Testing Capabilities
Modern diagnostic and measurement tools have become affordable enough for home use, allowing DIY labs to conduct testing that was previously only possible in professional settings. These capabilities transform subjective impressions into objective data that can guide decision-making and validate results.
Affordable precision measurement tools allow home enthusiasts to quantify performance changes and validate modifications with the same accuracy previously available only to professional shops or racing teams. Data logging capabilities capture information during actual driving or testing conditions, providing insights into real-world performance that static measurements can’t reveal. Comparison testing between different configurations or components provides objective data for decision-making rather than relying on subjective impressions or manufacturer claims.
Creating Controlled Testing Environments
Consistent, repeatable results require controlled conditions that eliminate variables. Setting up proper testing environments is crucial for generating reliable data that can inform future decisions and be shared with other enthusiasts for validation and improvement.
Environmental controls for temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure ensure that test results reflect actual performance changes rather than varying conditions that could mask or exaggerate effects. Standardized testing procedures eliminate human variables and ensure that results can be compared across different sessions or shared with other enthusiasts for validation. Documentation of testing conditions and procedures allows others to replicate your experiments and verify results, building credibility and advancing collective knowledge within the DIY community.
Technology Integration and Future-Proofing
The automotive industry is undergoing rapid technological change. DIY auto labs must be designed to adapt to electric vehicles, advanced driver assistance systems, and software-defined vehicles while maintaining capability for traditional mechanical work. Future-proofing your setup ensures continued relevance as the industry evolves.
Electric vehicle preparation requires different safety protocols, specialized tools, and updated electrical knowledge that goes far beyond traditional automotive electrical work. Software and firmware management capabilities become essential as modern vehicles function essentially as computers with wheels, requiring diagnostic and programming abilities that extend beyond mechanical skills. Integration with autonomous vehicle systems will increasingly involve sensor calibration, software configuration, and system integration rather than purely mechanical tasks.
Electric Vehicle Preparation and Safety
Working on electric vehicles requires different safety protocols, specialized tools, and updated electrical knowledge. Preparing your space for EV work is essential for future relevance as the automotive industry transitions away from internal combustion engines. Safety considerations become even more critical when dealing with high-voltage systems.
Proper electrical grounding systems and high-voltage safety equipment are essential for safe EV work, as the voltages involved can be lethal if proper precautions aren’t followed. Updated insurance and safety protocols reflect the different risks associated with EV work, including fire suppression systems designed for lithium battery fires rather than traditional automotive fires. EV-specific diagnostic tools and parts supplier relationships become necessary as traditional automotive suppliers may not carry the components needed for electric vehicle maintenance and repair.
The DIY automotive landscape continues evolving with innovative projects. The “Tomcat Trike” from RideApart demonstrates how electric vehicle platforms are being adapted for custom DIY applications, though safety considerations remain paramount for high-voltage systems.
Software and Firmware Management
Modern vehicles are essentially computers with wheels. DIY labs need capabilities for software diagnosis, firmware updates, and programming that go far beyond traditional mechanical work. These software skills become as important as traditional mechanical abilities for working on contemporary vehicles.
Software diagnostic capabilities allow identification of problems that don’t have physical symptoms, requiring different troubleshooting approaches than traditional mechanical failures. Firmware update capabilities ensure that vehicle systems remain current and functional, as manufacturers increasingly rely on software updates to address problems and add features. Programming abilities for modules and systems become necessary for many repair and modification procedures, requiring investment in both tools and training that goes beyond traditional automotive education.
Integration with Autonomous Vehicle Systems
As vehicles become more autonomous, DIY work will increasingly involve sensor calibration, software configuration, and system integration rather than purely mechanical tasks. Understanding these systems becomes essential for maintaining and modifying vehicles that rely on complex sensor arrays and computer processing.
Sensor calibration procedures ensure that autonomous systems function correctly after any work that might affect sensor positioning or operation, requiring specialized equipment and procedures. Software configuration capabilities allow adjustment of autonomous system parameters and integration of aftermarket components without compromising safety or functionality. System integration knowledge becomes necessary for any modifications that might affect autonomous vehicle operation, requiring understanding of how different systems interact and depend on each other.
The Business Architecture of Professional DIY Operations
The most sophisticated diy garage operations function as small businesses even when they’re not formally commercial. Understanding business principles – from workflow optimization to customer service – elevates DIY work from hobby to professional-grade operation. These principles create measurable improvements in efficiency, quality, and satisfaction.
Professional-level DIY operations use industrial engineering principles to optimize workflow, reduce waste, and improve quality, creating dramatic improvements in efficiency and results while reducing frustration. Understanding the economics of DIY automotive work helps optimize decisions about time investment, skill development, and equipment purchases that many enthusiasts make poorly due to lack of systematic analysis.
Workflow Engineering and Process Optimization
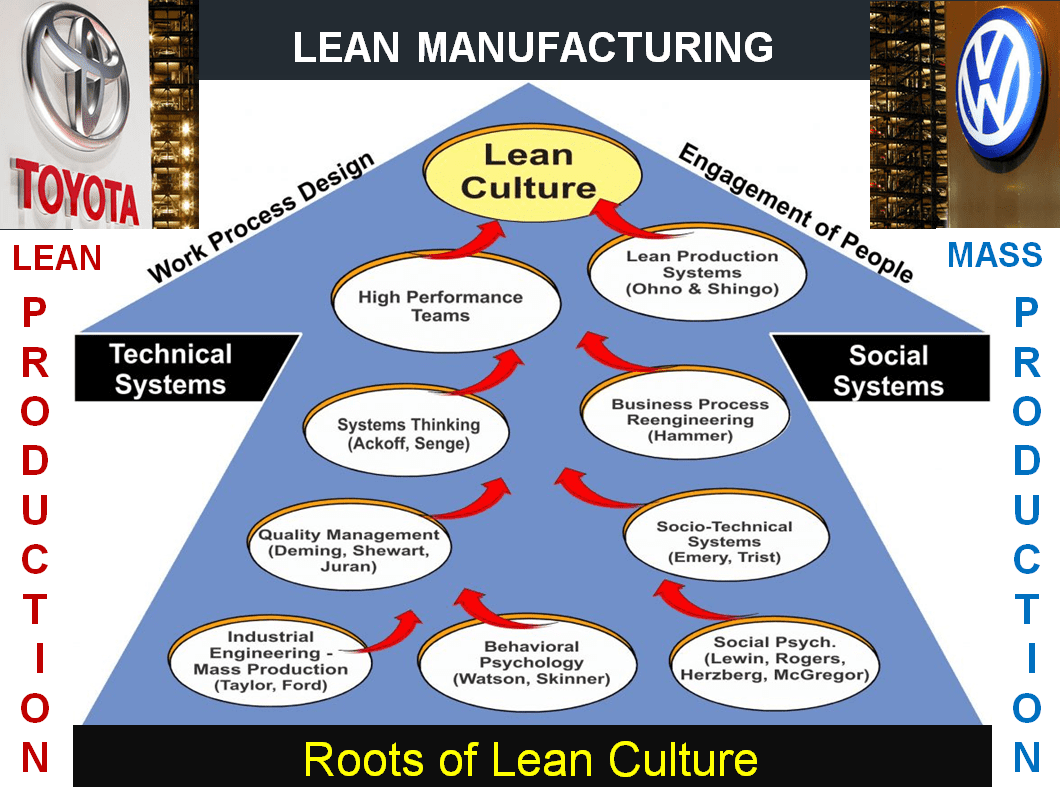
Professional-level DIY operations use industrial engineering principles to optimize workflow, reduce waste, and improve quality. These methods, borrowed from manufacturing and service industries, can dramatically improve efficiency and results while reducing the frustration and wasted time that plague many DIY enthusiasts.
Lean manufacturing concepts adapted for garage use create dramatic improvements in efficiency and quality while reducing the frustration that comes from disorganized workflows and repeated mistakes. Quality management principles ensure consistent results and help identify areas for improvement, preventing the inconsistent outcomes that plague many DIY enthusiasts and reducing the need to redo work. Customer service principles applied to personal projects improve satisfaction and outcomes by creating accountability and higher standards, even when you’re working on your own vehicles.
Implementing lean principles often requires starting with comprehensive decluttering services to remove the accumulated inefficiencies that prevent optimal workflow in your garage.
Lean Manufacturing Principles in Garage Operations
Lean manufacturing concepts can be adapted for garage use, creating dramatic improvements in efficiency and quality while reducing frustration and wasted time. The 5S methodology, kanban systems, and continuous improvement principles work as well in home garages as they do in professional manufacturing environments.
The 5S methodology (Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) creates systematic organization that reduces time spent searching for tools and materials while improving safety and work quality. Kanban systems for parts and supplies ensure that necessary materials are available when needed without overstocking or running out at critical moments during projects.
Continuous improvement principles create systematic approaches to identifying and eliminating inefficiencies, ensuring that your processes get better over time rather than remaining static. Visual management techniques make workflow status and resource availability immediately apparent, reducing mental overhead and decision-making time during projects.
Research from Webfoot Home shows that homeowners who implement systematic organization report spending 60% less time searching for tools and materials, directly correlating with improved project completion rates and reduced frustration.
Quality Management Systems for DIY Work
Implementing quality management principles ensures consistent results and helps identify areas for improvement. This systematic approach prevents the frustration of inconsistent outcomes that plague many DIY enthusiasts while building confidence in your abilities and results.
Standardized procedures ensure that successful approaches are repeated consistently rather than relying on memory or improvisation that can lead to variable results. Quality checkpoints throughout projects catch problems early when they’re easier and less expensive to correct, preventing the need to redo significant amounts of work. Root cause analysis of problems and failures prevents recurring issues by addressing underlying causes rather than just symptoms, improving long-term reliability and reducing frustration.
Customer Service Principles for Personal Projects
Even when working on your own vehicles, applying customer service principles improves satisfaction and outcomes. Treating yourself as a valued customer creates accountability and higher standards while making the work more enjoyable and professionally satisfying.
Clear project scoping and timeline management prevent the scope creep and endless projects that can drain motivation and resources while creating realistic expectations for completion. Documentation and communication standards ensure that you can pick up projects after interruptions and understand what work has been completed and what remains to be done. Quality standards and acceptance criteria provide objective measures of project completion and success, preventing the perfectionism that can prevent projects from ever being finished.
A DIY enthusiast implemented formal project documentation and quality checkpoints for his classic car restoration, reducing project timeline from an estimated 3 years to 18 months while improving build quality and maintaining detailed records that increased the vehicle’s resale value by 40%.
Economic Models and Value Creation
Understanding the economics of DIY automotive work helps optimize decisions about time investment, skill development, and equipment purchases. Many enthusiasts make poor economic choices due to lack of systematic analysis of costs, benefits, and opportunity costs involved in different approaches to automotive work.
Time value analysis helps determine when DIY work makes economic sense versus when outsourcing would be more cost-effective, considering both direct costs and opportunity costs of time investment. Systematic documentation of procedures, modifications, and solutions creates intellectual property that has value beyond immediate use and can be monetized through various channels.
Understanding the economics of DIY work includes knowing when to invest in professional appliance pick-up services rather than spending valuable project time on equipment disposal tasks.
Time Value Analysis and Skill ROI
Not all DIY work makes economic sense. Understanding when to DIY versus when to outsource requires analysis of time value, skill requirements, and learning benefits that most enthusiasts never perform systematically. This analysis helps optimize the allocation of time and resources for maximum benefit.
Calculating your effective hourly rate and comparing it to professional service costs provides a baseline for economic decision-making, though learning benefits and personal satisfaction may justify projects that don’t make pure economic sense. Estimating total project time including learning curves prevents underestimating the true cost of DIY work and helps set realistic expectations for project completion.
Factoring in tool and equipment costs that may only be used for single projects helps determine whether purchasing specialized tools makes economic sense or whether outsourcing would be more cost-effective. Evaluating long-term skill building benefits helps justify projects that may not make immediate economic sense but contribute to capabilities that will provide value on future projects.
Building Intellectual Property Assets
Systematic documentation of procedures, modifications, and solutions creates intellectual property that has value beyond immediate use. This knowledge can be monetized through teaching, consulting, or content creation while also providing personal reference materials that improve efficiency on future projects.
Detailed documentation of successful procedures and modifications creates valuable reference materials that can be shared, sold, or used to establish expertise and credibility within the automotive community. Problem-solving approaches and troubleshooting methods developed through experience become valuable intellectual property that can be taught to others or applied to consulting opportunities. Systematic knowledge organization makes your expertise accessible and valuable to others while also improving your own ability to apply lessons learned to new situations and challenges.
YouTube channels focused on DIY automotive content can generate substantial revenue, with established creators earning millions of subscribers and significant advertising revenue from systematically documenting and sharing their automotive expertise.
The Micro-Economics of Tool Ecosystem Development
Beyond individual tool purchases lies a complex ecosystem where equipment choices create cascading effects on capability, efficiency, and future options. Master-level DIY operations understand that tools function as interconnected systems rather than isolated purchases, requiring strategic thinking about compatibility, upgradeability, and ecosystem lock-in effects that can significantly impact long-term costs and capabilities.
Major tool manufacturers employ sophisticated strategies to create customer dependency through battery platforms, proprietary attachments, and exclusive software systems that can lead to costly platform migrations if not understood and planned for strategically. Advanced practitioners develop sophisticated battery management systems and precision measurement capabilities that leverage multiple manufacturer platforms while minimizing redundancy and maximizing capability per dollar invested.
Platform Dependency and Vendor Lock-In Strategies
Major tool manufacturers employ sophisticated strategies to create customer dependency through battery platforms, proprietary attachments, and exclusive software systems. Understanding these tactics allows DIY operators to make informed decisions about long-term equipment investments and avoid costly platform migrations that can waste thousands of dollars in redundant equipment.
Battery platform strategies create ongoing dependency through proprietary charging systems and tool compatibility, making it expensive to switch manufacturers once you’ve invested in a particular ecosystem. Proprietary software integration creates hidden ongoing costs and capability limitations that may not be apparent at initial purchase but can significantly impact long-term operational flexibility and costs. Strategic multi-platform approaches can minimize vendor lock-in while maximizing capability, but require careful planning and analysis of actual usage patterns and long-term needs.
Multi-Platform Battery Arbitrage Systems
Advanced practitioners develop sophisticated battery management systems that leverage multiple manufacturer platforms while minimizing redundancy and maximizing capability per dollar invested. This approach requires strategic thinking about power requirements, usage patterns, and cross-platform compatibility options.
Analysis of actual usage patterns across all current tools reveals opportunities for platform consolidation and identifies tools that justify separate battery platforms due to unique requirements or superior performance. Total cost of ownership calculations over 5-year periods include initial tool costs and battery replacement, charger requirements, and platform-specific accessories that can significantly impact long-term economics.
Cross-platform adapter opportunities and limitations must be evaluated carefully, as adapters may compromise performance or safety while providing compatibility between different battery systems. Charging station layouts that minimize downtime require strategic placement and capacity planning to ensure that batteries are always available when needed without excessive investment in redundant charging equipment.
Proprietary Software Integration Challenges
Modern automotive tools increasingly rely on proprietary software that creates hidden ongoing costs and capability limitations. Strategic software management becomes crucial for maintaining operational independence and avoiding unexpected costs or capability restrictions that can impact your ability to complete projects.
Software licensing costs and update requirements can create ongoing expenses that weren’t apparent at initial purchase, potentially making tools more expensive over time than initially calculated. Proprietary software systems may limit your ability to integrate tools with other systems or share data between different platforms, reducing the overall value and flexibility of your tool investments. Strategic software management includes evaluating open-source alternatives, planning for software obsolescence, and maintaining operational independence from any single vendor’s software ecosystem.
Advanced Calibration and Precision Measurement
Professional-grade DIY operations require measurement capabilities that extend beyond basic hand tools. Developing precision measurement systems enables work quality that rivals professional shops while building diagnostic capabilities that compound over time. These systems require understanding of calibration, environmental compensation, and statistical process control.
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure affect precision measurements in ways that most DIY practitioners never consider, but implementing compensation dramatically improves accuracy and repeatability. Establishing measurement traceability to national standards through calibration protocols ensures that precision work meets professional specifications and maintains accuracy over time. Statistical process control methods allow DIY operators to identify trends, predict failures, and maintain consistent quality levels across multiple projects and extended time periods.
Environmental Compensation in Measurement Systems
Temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure affect precision measurements in ways that most DIY practitioners never consider. Implementing environmental compensation dramatically improves accuracy and repeatability while ensuring that measurements remain valid across different conditions and seasons.
Temperature effects on metal expansion and measurement tool accuracy can create significant errors in precision work, but systematic compensation allows accurate measurements across varying conditions. Humidity and atmospheric pressure changes affect both measurement tools and the components being measured, requiring understanding of these effects and appropriate compensation methods. Environmental monitoring and compensation systems can be implemented cost-effectively in home shops, providing professional-level measurement accuracy without the expense of climate-controlled facilities.
Traceability and Standards Compliance
Establishing measurement traceability to national standards through calibration protocols ensures that precision work meets professional specifications and maintains accuracy over time. This systematic approach to measurement quality provides confidence in results and enables work that meets professional standards.
Calibration protocols ensure that measurement tools maintain accuracy over time and provide traceable references to national standards, enabling professional-quality work and documentation. Calibration service relationships and in-house calibration capabilities balance cost and convenience while ensuring that critical measurement tools remain accurate and reliable. Documentation and tracking systems for calibration ensure that measurement quality is maintained systematically rather than relying on memory or informal approaches that can lead to accuracy degradation over time.
Statistical Process Control for DIY Operations
Implementing statistical process control methods allows DIY operators to identify trends, predict failures, and maintain consistent quality levels across multiple projects and extended time periods. These techniques provide objective measures of process performance and help identify opportunities for improvement.
Control charts and statistical analysis of measurement data reveal trends and variations that aren’t apparent from individual measurements, enabling proactive adjustments before problems occur. Process capability analysis helps determine whether your equipment and procedures are capable of meeting required specifications consistently, identifying areas where improvements are needed. Predictive analysis based on historical data allows anticipation of tool maintenance needs and process adjustments before quality problems occur, reducing waste and improving reliability.
When your DIY garage operation reaches this level of sophistication, you’ll inevitably face a challenge that even the most organized enthusiasts struggle with: managing the accumulation of obsolete equipment, failed project materials, and outdated technology that can overwhelm even well-planned spaces.
Jiffy Junk’s professional cleanout services understand the unique needs of advanced DIY operations. Unlike general junk removal, automotive spaces require expertise in handling hazardous materials, identifying valuable components that shouldn’t be discarded, and understanding which materials require special disposal protocols.
Ready to optimize your garage space for peak performance? Contact Jiffy Junk today for a consultation on professional garage cleanout services that will give you the clean slate needed to implement these advanced systems effectively.
Final Thoughts
Your DIY garage represents far more than a place to fix cars – it’s a complex system where psychology, technology, business principles, and economics intersect to either amplify or limit your capabilities. The difference between amateur and professional-grade operations isn’t just about having better tools; it’s about understanding and implementing the invisible systems that multiply your effectiveness.
The most successful DIY enthusiasts recognize that their garage is simultaneously a laboratory, a business, and a personal development environment. Each project becomes an opportunity to refine systems, build knowledge assets, and develop capabilities that compound over time. This systematic approach transforms automotive work from a series of isolated tasks into a coherent practice that builds expertise and creates value.
As the automotive industry continues evolving toward electric vehicles, autonomous systems, and software-defined functionality, the principles outlined here become even more critical. The DIY enthusiasts who thrive in this changing landscape will be those who’ve built adaptable systems and developed learning capabilities that can evolve with new technologies and challenges.
The integration of psychological principles, business systems, and advanced technology creates a multiplier effect where each element enhances the others, resulting in capabilities that exceed the sum of individual improvements. Future success in DIY automotive work will depend more on systematic thinking and adaptability than on specific technical knowledge, as the pace of technological change makes continuous learning essential. The investment in systems and infrastructure pays dividends across all future projects, making the initial effort to implement these approaches one of the highest-return activities any serious DIY enthusiast can undertake.