DIY Septic System Installation: The Underground Economics That Could Save You Thousands
Table of Contents
- The Hidden Financial Ecosystem Behind DIY Septic Systems
- Navigating the Regulatory Gray Zone Without Getting Burned
- Mastering the Secondary Market for Septic Components
- Material Science Secrets for Long-Lasting Systems
- Engineering Challenges at the Micro Scale
- Lifecycle Economics: The True Cost of DIY Installation
- Strategic Timing for Maximum Success
- The Social Engineering Side of Septic Projects
- How Professional Cleanup Services Support Your DIY Project
- Final Thoughts
TL;DR
- DIY septic systems involve complex financial calculations beyond simple installation costs, including permit arbitrage opportunities and regulatory compliance trade-offs
- The secondary market for septic components offers significant savings through industrial surplus dealers and food-grade container networks
- Material science knowledge helps you select components that resist septic environment degradation and extend system longevity
- Small-scale systems require different engineering approaches, especially for RV installations and confined space applications
- Strategic timing based on seasonal conditions, regulatory cycles, and market dynamics can dramatically impact project success and costs
- Neighbor relations and contractor management are crucial social elements that determine project feasibility and long-term success
The Hidden Financial Ecosystem Behind DIY Septic Systems
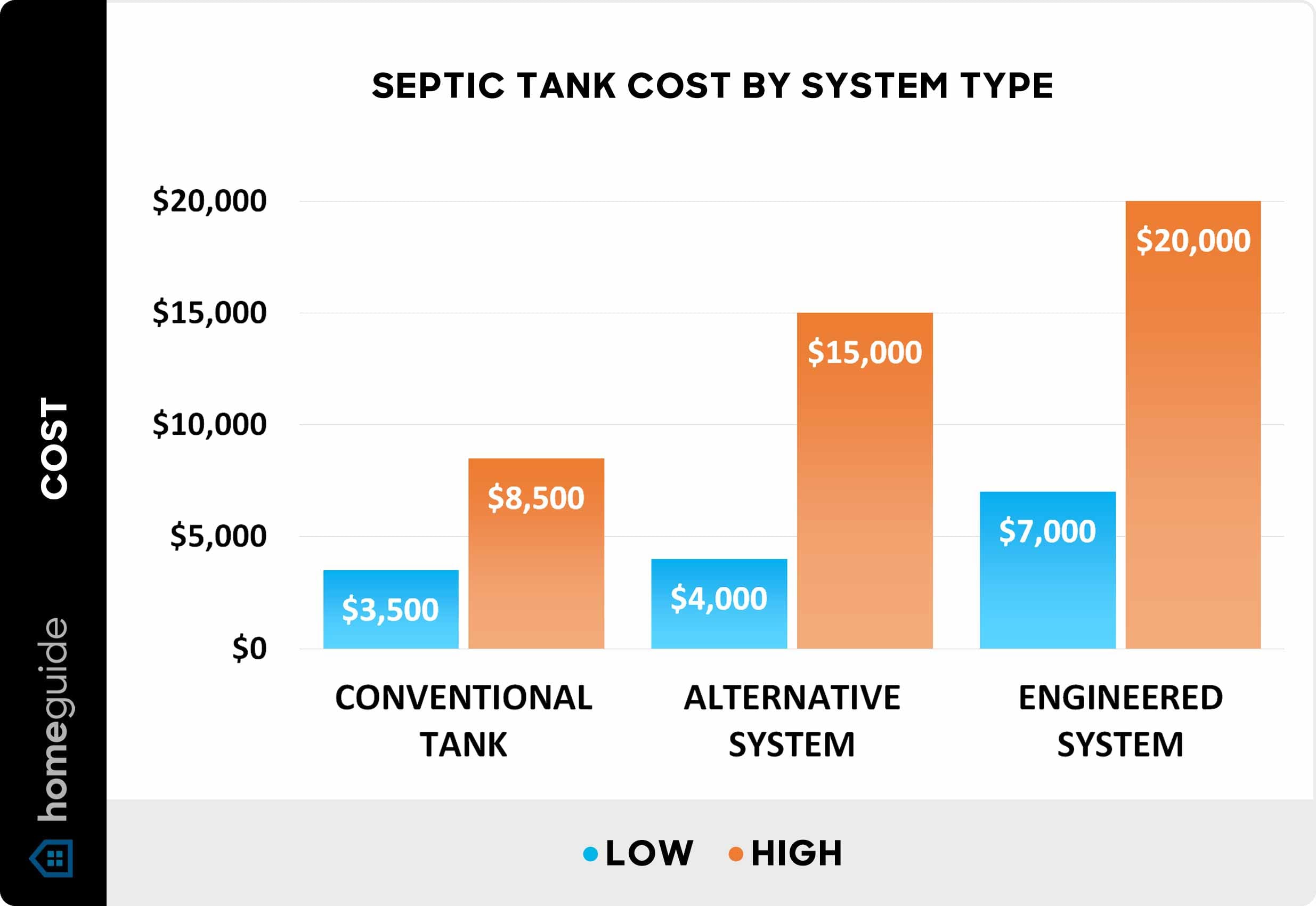
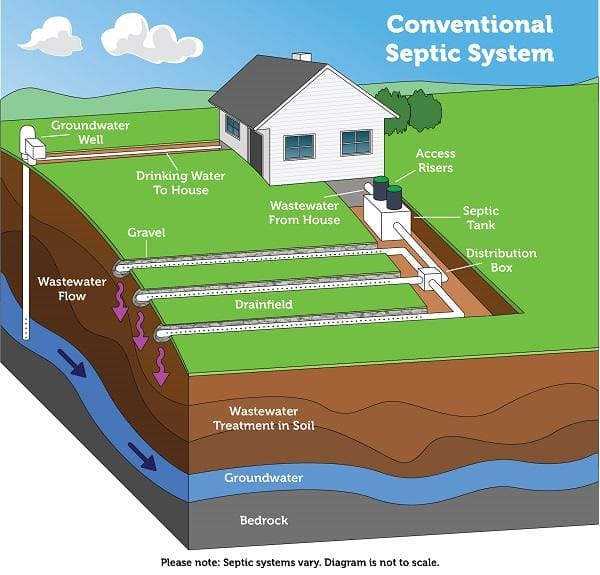
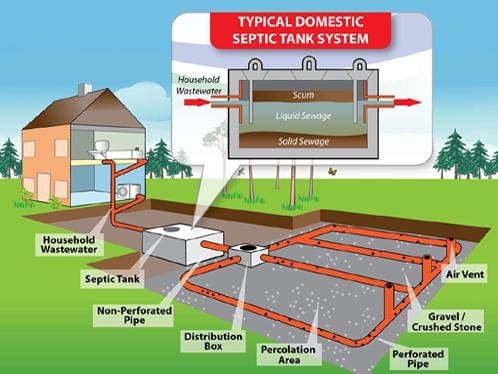
I’ve spent years watching homeowners get blindsided by the true costs of septic installation. The average home with three bedrooms and two bathrooms typically requires a 1,000-gallon septic tank, according to the University of Georgia Extension. But here’s what most people don’t realize – the financial landscape around diy septic system projects goes way deeper than just comparing contractor quotes to material costs.
When I talk about regulatory arbitrage, I’m referring to something most homeowners never consider. Rural areas often have completely different enforcement patterns than urban municipalities. I’ve seen people save thousands by understanding these differences and timing their projects accordingly. The key is recognizing that enforcement varies dramatically between jurisdictions, and smart homeowners can exploit these differences legally.
The financial calculus gets complicated when you factor in property sale implications and insurance coverage. I’ve watched diy septic system installations affect property values in unexpected ways. Sometimes a well-documented DIY installation actually increases buyer confidence because they can see exactly what was done and how. Other times, the lack of professional installation records creates problems during real estate transactions.
What really gets expensive are the hidden costs that nobody talks about upfront. Permit fees can range from $200 to $2,000 depending on your location. Inspection schedules might require multiple visits at $150 each. Then there’s the long-term maintenance cost differential between compliant and non-compliant installations. A cheap diy septic system might save money initially, but if it fails inspection later, you’re looking at complete replacement costs.
Understanding Permit Requirements and Enforcement Patterns
Septic regulations exist in this weird web of overlapping authority. Local health departments, state environmental agencies, and sometimes federal oversight all have their fingers in the pie. I’ve navigated this maze dozens of times, and success really comes down to understanding the personalities and priorities of your local officials rather than just reading the regulations.
Research your local health department’s inspection schedule and backlog. I’ve seen permit applications sit for months during busy seasons, but get processed in days during slow periods. Document existing system conditions with photographs and measurements before you start anything. This creates a paper trail that shows you’re making improvements, not just cutting corners.
Recent legislative changes in Indiana highlight how the regulatory landscape keeps shifting. House Bill 1647 would grant Hoosier property owners the ability to override local health department decisions about new septic system installations, according to the Indiana Capital Chronicle. This demonstrates how regulatory frameworks continue moving toward property owner autonomy over traditional health department oversight.
Building relationships with local officials pays dividends. I know a guy who brings donuts to the health department every few months. Sounds silly, but when his permit application needed quick turnaround, guess whose paperwork got priority attention? These people deal with frustrated homeowners all day – being pleasant and prepared makes you memorable for the right reasons.
The Economics of Compliance Versus Risk
Here’s where things get really interesting from a financial perspective. The decision between full compliance and alternative approaches requires honest risk assessment. You need to calculate the probability of enforcement action in your specific area, then weigh that against the cost difference between compliant and non-compliant installations.
I’ve created a framework for this analysis that considers multiple factors. Calculate total compliance costs including permits, inspections, and professional oversight. Then research enforcement patterns in your area – how often do they actually check existing systems? What triggers investigations? Property sales? Neighbor complaints? System failures?
Property insurability becomes a major factor that most people overlook. Non-compliant systems can create significant obstacles during real estate transactions. I’ve seen deals fall through because buyers couldn’t get insurance on properties with questionable septic systems. The cost savings from cutting corners can evaporate quickly when you’re forced to install a compliant system to close a sale.
| Compliance Level | Initial Cost | Risk Factor | Long-term Value Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Compliance | $8,000-$12,000 | Low | Positive property value |
| Partial Compliance | $5,000-$8,000 | Medium | Neutral to slight negative |
| Non-Compliance | $2,000-$5,000 | High | Significant negative impact |
| DIY with Professional Oversight | $4,000-$7,000 | Low-Medium | Positive with documentation |
Navigating the Regulatory Gray Zone Without Getting Burned
The regulatory landscape around diy septic system projects operates in shades of gray rather than black and white. I’ve learned that success depends more on understanding the human element behind regulations than memorizing code requirements. Most enforcement happens reactively – someone complains, a system fails visibly, or a property changes hands.
Regulatory arbitrage occurs when you exploit differences in enforcement between jurisdictions. Rural areas often have more lenient oversight than urban municipalities simply because they have fewer inspectors covering larger territories. I’ve seen identical installations get completely different treatment based solely on which side of a county line they’re located.
The financial calculus must factor in property sale implications, insurance coverage, and potential liability exposure when weighing compliance versus non-compliance decisions. This isn’t just about saving money upfront – it’s about understanding the long-term financial implications of your choices.
Total project costs include hidden expenses that can double your initial budget if you’re not careful. Permit fees, inspection schedules, and the long-term maintenance cost differential between compliant and non-compliant installations all add up. A diy septic system that seems affordable initially might become expensive if you need to bring it up to code later.
Mastering the Secondary Market for Septic Components
The septic component market operates on multiple levels that most homeowners never discover. Beyond the obvious retail suppliers, there’s a whole underground economy of industrial surplus dealers, decommissioned system components, and specialty networks that can dramatically reduce your project costs.
Industrial facilities regularly upgrade their waste treatment systems, creating opportunities to acquire high-quality components at a fraction of retail cost. I’ve sourced concrete tanks, pumps, and control systems from food processing plants, manufacturing facilities, and commercial buildings for 20-30% of retail pricing. These components often exceed residential requirements, providing built-in redundancy and longevity.
Commercial and industrial systems typically get over-engineered for liability reasons. When a brewery replaces their waste treatment system, the old components might be rated for much higher capacity and chemical resistance than you’ll ever need. This over-specification works in your favor for diy septic system applications.
Professional networks become valuable contacts for accessing surplus equipment. Facility maintenance managers, environmental consultants, and industrial contractors all know when systems are being upgraded or decommissioned. Building these relationships takes time, but the savings opportunities are substantial.
Industrial Surplus and Decommissioned Systems
Commercial and industrial facilities regularly upgrade their waste treatment systems, creating opportunities to acquire high-quality components at fraction of retail cost. I’ve built relationships with facility maintenance managers at local industrial sites to gain access to their upgrade and replacement schedules.
Monitoring commercial construction and demolition projects reveals when waste treatment systems are being removed or replaced. I keep track of major construction projects in my area and contact the general contractors about salvaging septic components before they hit the dumpster.
A food processing plant in Ohio replaced their 5,000-gallon primary treatment tank with a newer model, selling the original concrete tank for $800 instead of the $3,500 retail price for a comparable residential unit. The industrial-grade reinforcement and chemical-resistant coating provided superior longevity compared to standard residential tanks. Even after transportation costs, the savings made the sourcing effort worthwhile for this diy septic system project.
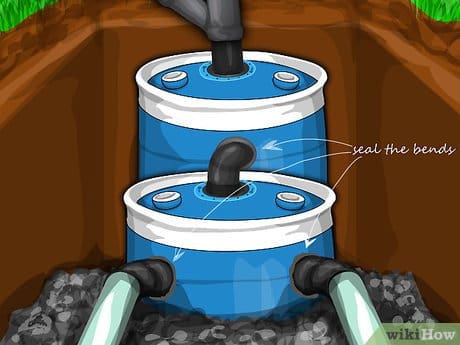
The 55-Gallon Drum Underground Economy
The popularity of 55 gallon drum septic system installations reflects both their affordability and the robust secondary market for food-grade containers. I’ve found that success depends on understanding subtle differences between container types and their suitability for septic applications.
Verify food-grade certification and previous contents to ensure chemical compatibility with septic effluent. I’ve seen people use drums that previously contained industrial chemicals, creating contamination issues that cost more to remediate than buying proper containers initially. Always ask for documentation about previous contents and cleaning procedures.
Assess wall thickness and structural integrity since septic applications create different stress patterns than original food storage use. The constant moisture, soil pressure, and bacterial activity can cause failures in containers that seemed perfectly adequate for their original purpose.
The growing DIY waste management trend extends beyond septic systems to pet waste management. These DIY dog waste composters divert dog waste from landfills and keep it in your own backyard in an environmentally friendly way. They work similarly to a home septic system, according to Kinship. This demonstrates how septic system principles are being adapted for smaller-scale waste management applications, creating additional markets for components and expertise.
Material Science Secrets for Long-Lasting Systems
Traditional septic guides focus on installation techniques while completely overlooking the material science that determines whether your system lasts 10 years or 30 years. I’ve learned that understanding polymer degradation, chemical resistance, and thermal expansion characteristics allows you to make informed decisions that can save thousands in replacement costs.
Septic systems create unique chemical environments with anaerobic bacteria and hydrogen sulfide that accelerate certain types of material degradation. Standard PVC might last decades in a water supply application but fail within years in septic effluent. Understanding these interactions helps you select components that will actually survive the environment they’re installed in.
Chemical resistance ratings must be evaluated for your specific soil chemistry. Ground conditions vary significantly and affect material performance in ways that generic ratings don’t capture. I always test soil pH and chemical composition before selecting materials, especially for underground components that can’t be easily replaced.
Thermal expansion characteristics become critical in climate zones with significant temperature variations. I’ve seen rigid piping systems fail because nobody accounted for the expansion and contraction cycles that occur with seasonal temperature changes. Flexible connections and expansion joints prevent these failures.
The state health department estimates that approximately 200,000 septic disposal systems are inadequate, have failed or are in the process of failing according to the Indiana Capital Chronicle. This emphasizes the critical importance of proper material selection and installation techniques for long-term diy septic system viability.
Understanding chemical compatibility becomes particularly important when sourcing alternative materials for your diy septic system. Many industrial polymers offer superior performance characteristics compared to residential-grade components, but require careful evaluation of their interaction with septic effluent chemistry. I’ve used chemical-resistant polymers from industrial applications that cost less than residential components while providing better performance.
Polymer Degradation in Septic Environments
Septic systems create unique chemical environments that accelerate certain types of material degradation while preserving others. The interaction between anaerobic bacteria, hydrogen sulfide, and various polymers creates predictable failure patterns that you can mitigate through proper material selection.
Evaluate chemical resistance ratings for your specific soil chemistry and consider UV degradation for above-ground components exposed to sunlight. I’ve seen expensive control panels fail because nobody considered that UV exposure would degrade the plastic housing within a few years.
Plan replacement intervals based on material science data rather than manufacturer warranties. Warranties often don’t account for septic-specific conditions, so they’re not reliable indicators of actual service life in your diy septic system application.
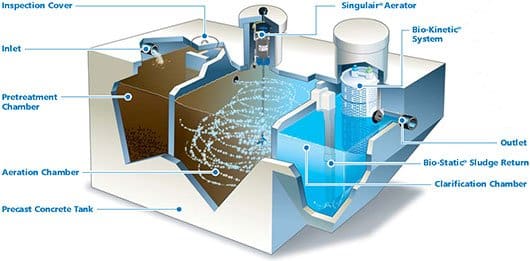
High-Performance Polymer Alternatives to Concrete
While concrete remains the gold standard for septic tanks, high-performance polymers offer advantages in specific installations. These materials provide superior chemical resistance and can be installed in locations where concrete placement is impractical due to access limitations or soil conditions.
Reduced installation weight eliminates heavy equipment requirements and allows installation in areas with limited access or unstable soil conditions. I’ve installed polymer tanks in locations where getting a concrete truck would have been impossible or prohibitively expensive.
Superior resistance to ground movement and settling prevents the cracking and structural failures common in concrete installations. In areas with expansive clay soils or freeze-thaw cycles, polymer tanks often outlast concrete alternatives.
When upgrading from older systems, proper disposal of legacy components through appliance disposal services ensures environmental compliance and site preparation for new installations.
Engineering Challenges at the Micro Scale
DIY septic systems require understanding engineering principles that operate at multiple scales, from bacterial colonies to hydraulic flow patterns. This gets particularly complex when working with small septic system installations or unconventional applications where traditional design assumptions don’t apply.
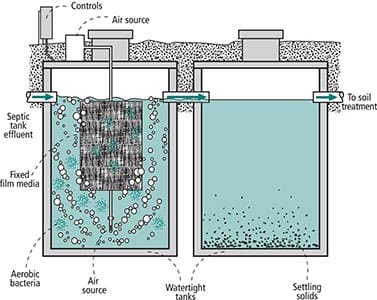
Small septic systems present unique engineering challenges that require different approaches than simply scaling down conventional designs. The physics of bacterial processing, hydraulic retention time, and effluent quality all change dramatically at smaller scales. Surface area to volume ratios create different treatment dynamics that affect bacterial populations and processing efficiency.
Understanding these principles allows for system optimization that maximizes treatment efficiency within space constraints. I’ve designed small septic tank installations that outperform larger conventional systems because they’re engineered specifically for their operating conditions rather than just scaled down from larger designs.
Bacterial loading calculations must account for the unique characteristics of small-scale installations. The bacterial ecology in a 300-gallon tank operates differently than in a 1,500-gallon tank, requiring different approaches to nutrient balance and waste loading to maintain healthy bacterial populations.
Small-Scale System Design and Optimization
Small septic systems create different bacterial environments than larger systems, requiring careful attention to loading rates, retention times, and nutrient balance. Understanding bacterial ecology principles allows for system optimization that maximizes treatment efficiency within space constraints.
Calculate optimal hydraulic retention time for your specific waste stream and design baffling systems to maximize contact time between waste and bacterial populations. I’ve used internal baffles and flow directors to increase effective retention time in compact installations without increasing tank size.
Implement staged treatment processes within space constraints and monitor bacterial populations through controlled feeding schedules. Small septic system installations benefit from more active management than larger systems because they have less buffer capacity for handling variations in loading.
Design specifications typically require 75 to 100 gallons per day per bedroom with 2 day tank capacity according to the Mobile Home University Forum. This provides the foundation for calculating appropriate system sizing for small-scale applications, but I’ve found that actual performance depends more on proper design than just meeting minimum capacity requirements.
| System Scale | Tank Size | Bedrooms Served | Retention Time | Bacterial Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro (RV) | 40-100 gal | 1 bedroom equiv | 1-2 days | 60-70% |
| Small Residential | 500-750 gal | 1-2 bedrooms | 2-3 days | 75-85% |
| Standard Residential | 1000-1500 gal | 3-4 bedrooms | 3-4 days | 85-95% |
| Large Residential | 1500+ gal | 5+ bedrooms | 4+ days | 90-95% |
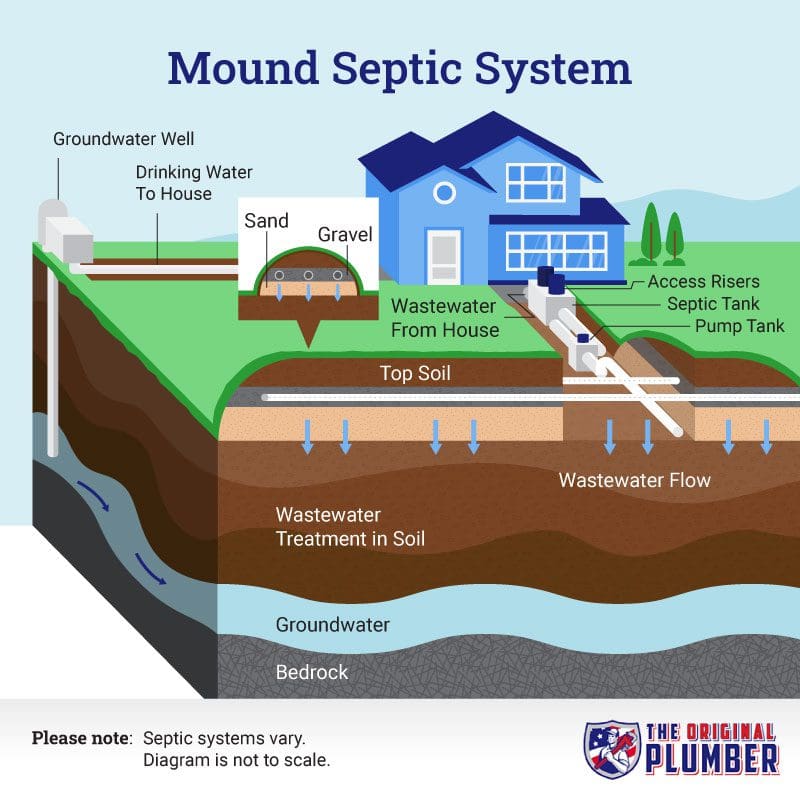
RV Integration and Mobile Applications
Installing permanent septic systems for RV use presents unique challenges that combine mobile home waste characteristics with permanent installation requirements. These systems must handle variable loading, extended vacancy periods, and different waste stream compositions than typical residential applications.
Account for variable occupancy patterns and loading rates that differ significantly from consistent residential use patterns. RV installations might see heavy use for weeks followed by complete vacancy for months. This creates challenges for maintaining bacterial populations and system function during dormant periods.
Design for extended dormancy periods without system failure and plan for seasonal maintenance and winterization requirements. I’ve incorporated recirculation systems and bacterial maintenance protocols that keep systems functional during extended vacancy periods.
A retired couple in Arizona installed a 750-gallon concrete tank system for their permanent RV site, designing it to handle 6-month occupancy periods followed by 3-month vacancy. They incorporated a recirculation pump system to maintain bacterial populations during vacancy periods and installed freeze protection for winter operation. This hybrid rv in ground septic tank system cost $3,200 compared to $8,500 for traditional installation while providing superior performance for their specific use pattern.
Hydraulic Engineering for Small Systems
Understanding fluid dynamics becomes critical when working with small-scale septic systems where traditional design assumptions may not apply. Laminar flow, retention time calculations, and effluent distribution all require different approaches at smaller scales to prevent dead zones and short-circuiting.
Model flow patterns using simple tracer studies to identify and eliminate dead zones through baffling modifications. I use food coloring or other safe tracers to visualize flow patterns in small systems and identify areas where waste might bypass treatment zones.
Optimize inlet and outlet configurations for your specific geometry and implement flow distribution systems for even loading across treatment areas. Small systems are particularly sensitive to flow distribution problems that might not affect larger installations significantly.
Lifecycle Economics: The True Cost of DIY Installation
The true cost of diy septic system installations extends far beyond initial installation costs. I’ve tracked the total ownership costs of dozens of installations over 10-15 year periods, and the results might surprise you. Understanding these lifecycle economics helps inform decisions about system design, component selection, and long-term planning.
DIY septic systems often require different maintenance approaches than professionally installed systems due to design differences and owner knowledge levels. The advantage is that DIY installers typically understand their systems better and can perform maintenance tasks that would require professional service calls for other homeowners.
Predictive maintenance strategies can significantly reduce lifecycle costs by preventing costly emergency repairs through proactive interventions. I’ve developed monitoring protocols that catch problems early when they’re still inexpensive to fix rather than waiting for complete system failures.
End-of-life planning must consider component recovery, recycling opportunities, and environmental impact mitigation strategies. Many septic system components retain significant value at end-of-life, and planning for recovery can offset replacement costs while reducing environmental impact.
Long-term financial planning should include provisions for technology upgrades and regulatory changes that may affect your diy septic system over its operational lifetime. I’ve seen regulatory changes require expensive upgrades to existing systems, and planning for these possibilities helps avoid financial surprises.
Predictive Maintenance Strategies
DIY installers have the advantage of intimate system knowledge, allowing for predictive maintenance approaches that can significantly reduce lifecycle costs. Understanding failure modes and their precursors enables proactive interventions that prevent costly emergency repairs.
Document all system components and their expected service lives, then establish monitoring protocols for key performance indicators. I maintain detailed records of every component in my systems, including installation dates, expected service lives, and performance benchmarks that help identify when components are approaching failure.
Create maintenance schedules based on actual usage patterns rather than generic recommendations that may not match your specific installation. Generic maintenance schedules assume average usage patterns that might not apply to your situation, leading to either excessive maintenance costs or inadequate system care.
DIY Septic System Maintenance Checklist:
- ☐ Monthly visual inspection of access ports
- ☐ Quarterly effluent quality assessment
- ☐ Semi-annual sludge level measurement
- ☐ Annual bacterial population evaluation
- ☐ Biennial soil percolation testing
- ☐ 3-5 year professional system evaluation
Regular maintenance often generates waste materials that require proper disposal, making scrap metal pickup services valuable for disposing of old pumps, pipes, and other system components safely.
System Expansion Economics
Many DIY installations begin as minimal systems that require expansion as needs change. Understanding the economics of system expansion helps inform initial design decisions and long-term planning, including utility routing and regulatory considerations that affect future modification options.
Design initial systems with expansion capabilities and plan utility routing and access for future modifications. I always install oversized distribution boxes and leave expansion ports even in minimal initial installations because adding capacity later is much more expensive than planning for it initially.
Consider regulatory changes that might affect expansion options and evaluate the economics of replacement versus expansion. Sometimes it’s more cost-effective to replace an entire small system than to expand it, especially if regulatory requirements have changed since the original installation.
End-of-Life Planning and Environmental Responsibility
DIY septic systems eventually require replacement or major renovation, creating waste streams that must be managed responsibly. Understanding component recovery options and environmental impact mitigation strategies can offset replacement costs while reducing environmental footprint.
Many septic system components retain value at end-of-life as recyclable materials or components suitable for reuse in other applications. Concrete tanks can be broken up for aggregate, metal components have scrap value, and some plastic components can be recycled through specialized programs.
Plan for safe removal and transportation of recoverable materials and establish relationships with recycling facilities and reuse markets. I’ve developed relationships with concrete recyclers, scrap metal dealers, and specialty plastic recyclers that help offset replacement costs while ensuring responsible disposal.
Strategic Timing for Maximum Success
Understanding when to undertake diy septic system installation involves strategic timing based on seasonal conditions, regulatory cycles, and market dynamics. This timing strategy extends beyond simple weather considerations to include soil microbiology, permit processing speeds, and material availability patterns.
Seasonal timing involves complex factors including soil bacterial population recovery, permit processing speeds, and material availability that create distinct advantages for different installation windows. I’ve learned that spring installations benefit from natural bacterial population increases, while fall installations offer reduced competition for permits and inspections.
Regulatory agencies operate on predictable cycles that create opportunities for strategic timing of permit applications and inspections. Budget cycles affect staffing, inspection frequency, and enforcement priorities, creating windows of opportunity for different types of applications.
Planning your installation timeline should also consider yard waste disposal schedules for clearing vegetation and organic matter from your installation site.
Seasonal Installation Windows
Spring installation coincides with soil bacterial population recovery after winter dormancy, allowing new septic systems to establish bacterial colonies during optimal conditions. The warming soil temperatures and increasing microbial activity create ideal conditions for system startup and bacterial establishment.
Summer provides peak performance conditions but requires careful attention to excavation timing and material costs during peak construction season. I’ve found that early summer offers the best balance of favorable conditions and reasonable material costs before peak construction demand drives prices up.
Fall installation offers reduced competition for permits and inspections, cooler working conditions, and end-of-season material pricing opportunities. Many suppliers offer discounts on inventory they don’t want to carry through winter, creating cost savings opportunities for diy septic system projects.
Regulatory Cycle Timing
Most regulatory agencies operate on fiscal year budgets that affect staffing, inspection frequency, and enforcement priorities. These cycles create windows of opportunity for different types of applications and installations when agencies have adequate resources and reduced application volumes.
Submit applications during low-activity periods for faster processing and schedule inspections when agencies have adequate staffing. I’ve found that mid-fiscal year typically offers the best balance of adequate staffing and reasonable workloads for most agencies.
Plan installations during periods of reduced enforcement activity and coordinate with agency planning cycles for optimal timing. Understanding when agencies are focused on other priorities can help you avoid unnecessary scrutiny while still maintaining compliance with applicable regulations.
The Social Engineering Side of Septic Projects
Successful diy septic system installation often depends as much on managing relationships with neighbors, contractors, and officials as on technical execution. I’ve seen technically perfect installations fail because of social problems, and marginal installations succeed because the homeowner managed relationships effectively.
Septic installation affects property values, aesthetics, and sometimes shared resources in ways that can create lasting neighborhood tensions. Proactive communication about your project timeline, potential disruptions, and mitigation measures helps prevent conflicts before they start.
Proactive neighbor relations can prevent conflicts while creating opportunities for mutual benefit through coordinated improvements. I’ve coordinated with neighbors to share equipment costs, coordinate utility work, and even negotiate bulk material purchases that benefit everyone involved.
Strategic use of professional services for specific project phases provides quality assurance while maintaining cost control. Even DIY installations benefit from professional input on critical aspects, and knowing when to bring in experts can prevent costly mistakes.
Coordinating with neighbors often involves managing shared cleanup responsibilities, where bulk trash removal services can facilitate community cooperation during large projects.
Neighbor Relations and Shared Resources
Many rural properties share access roads, utility easements, or drainage patterns that affect septic installation. Negotiating these shared interests requires understanding both legal rights and practical cooperation needs, including compensation for temporary inconveniences.
Research property boundaries and easement rights thoroughly and document existing conditions that might be affected by installation. I always survey property lines and photograph existing conditions before starting any work that might affect neighboring properties.
Identify potential mutual benefits from coordinated improvements and prepare compensation offers for temporary inconveniences. Sometimes offering to repair shared access roads or coordinate utility work can turn potential conflicts into cooperative relationships.
A homeowner in rural Vermont coordinated with three neighbors to share excavation equipment costs and schedule installations sequentially, reducing individual equipment rental costs from $1,200 to $400 per property. The coordination also allowed them to negotiate bulk pricing on concrete tanks and aggregate materials, saving an additional $800 per installation while building positive neighbor relationships for future maintenance cooperation.
Strategic Contractor Relationships
Even DIY installations often require some professional services, creating complex relationships where homeowners must balance cost control with quality assurance. Understanding contractor motivations and constraints enables more effective negotiations and project management.
Strategic use of professional services for specific project phases can provide quality assurance while maintaining cost control. I typically engage professionals for soil testing and site evaluation, consider professional excavation for complex installations, and maintain relationships for future maintenance needs.
Professional Service Integration Checklist:
- ☐ Soil percolation testing and site evaluation
- ☐ Permit application assistance and regulatory navigation
- ☐ Excavation for complex or deep installations
- ☐ Electrical connections and pump installations
- ☐ Final inspection preparation and documentation
- ☐ Emergency repair and maintenance contacts
When working with contractors, understanding construction waste disposal requirements helps ensure proper cleanup and compliance with local regulations throughout your project.
How Professional Cleanup Services Support Your DIY Project
DIY septic installation inevitably generates substantial amounts of waste material that requires proper disposal. From excavated soil and old septic components to packaging materials and construction debris, managing this waste stream can become overwhelming without proper planning.
Pre-installation cleanup creates clean workspace and ensures proper access for equipment and materials by removing existing debris and structures. I’ve found that starting with a clean, organized work area prevents delays and safety issues throughout the installation process.
During construction, ongoing debris removal prevents work area congestion and maintains safe working conditions. This becomes particularly valuable for larger excavation projects where debris accumulation can interfere with equipment operation and create safety hazards.
Post-installation services ensure old septic components, excess materials, and construction debris are properly recycled or disposed of according to environmental regulations. Many diy septic tank components require specialized disposal methods due to contamination concerns, and professional services understand these requirements.
Jiffy Junk specializes in construction debris removal and understands the unique waste streams generated by DIY septic projects. Our eco-friendly disposal practices ensure proper handling of contaminated soil, old concrete tanks, and chemical containers that require specialized disposal methods. We can coordinate pickup schedules around your project timeline, allowing you to focus on installation while we handle the cleanup logistics professionally and responsibly.
Ready to start your DIY septic project? Contact Jiffy Junk today to discuss debris removal services that support your installation timeline and budget.
Final Thoughts
DIY septic system installation represents a complex intersection of technical knowledge, financial strategy, and social navigation that extends far beyond simple plumbing work. The underground economics involve regulatory arbitrage opportunities, secondary market sourcing strategies, and lifecycle cost calculations that can save thousands of dollars when properly understood and executed.
Success requires mastering material science principles, understanding bacterial ecology at micro scales, and timing your project strategically around seasonal conditions and regulatory cycles. The social engineering aspects—managing neighbor relations, contractor relationships, and regulatory compliance—often determine project feasibility as much as technical competence.
Whether you’re considering a homemade septic system approach or developing comprehensive diy septic system plans, the key is thorough preparation and realistic assessment of your capabilities. From basic homemade septic tank construction to complex diy septic tank installations, every project benefits from strategic planning that considers all aspects of the installation process.
Most importantly, the true value of diy septic system installation lies in developing the knowledge and relationships that support long-term system maintenance and optimization. This comprehensive approach transforms a potentially risky DIY project into a strategic investment in property value and personal capability. Even the most cheap diy septic system approach requires attention to quality and long-term performance to achieve real savings.
The financial ecosystem of DIY septic systems creates opportunities for significant savings through regulatory arbitrage, secondary market sourcing, and strategic timing that most homeowners never discover. Technical success depends on understanding material science, bacterial ecology, and hydraulic engineering principles that operate differently at small scales than in commercial installations. Long-term value comes from developing maintenance expertise and professional relationships that support system optimization and prevent costly emergency repairs over the system’s lifecycle.