DIY Outdoor Kitchen Nightmares: The Critical Mistakes That’ll Cost You Thousands (And How to Avoid Them)
Most outdoor kitchens range between 100 and 400 square feet, according to the National Kitchen and Bath Association, but size alone doesn’t determine success. The difference between a functional outdoor cooking space and an expensive disaster lies in understanding the complex engineering challenges that most DIY builders completely ignore.
Table of Contents
-
Thermal Dynamics and Material Science in Outdoor Cooking Spaces
-
The Psychology of Outdoor Cooking Workflow
-
Infrastructure Integration and Hidden Utilities
-
Budget-Conscious Innovation Through Strategic Salvage
-
Regulatory Navigation and Code Compliance Strategies
TL;DR
-
Most DIY outdoor kitchen failures stem from ignoring thermal dynamics – metal frames create heat highways that make surfaces untouchable and cause structural damage through differential expansion
-
Outdoor kitchens create their own weather systems requiring strategic ventilation, humidity control, and radiant heat management that traditional indoor design principles can’t address
-
Underground utility planning must account for 50% excess capacity and future maintenance access, while greywater management prevents environmental violations
-
Commercial equipment adaptation and strategic material salvage can cut costs by 60-70% while delivering superior performance compared to residential outdoor appliances
-
Smart permit navigation and proper documentation can reduce insurance premiums while avoiding costly code compliance issues that shut down projects
Thermal Dynamics and Material Science in Outdoor Cooking Spaces
Building a successful DIY outdoor kitchen requires understanding complex thermal behavior that goes far beyond knowing grills get hot. I’ve seen too many beautiful outdoor kitchens become unusable disasters because builders ignored the invisible forces of heat transfer and material expansion.
Temperature variations create invisible challenges that destroy poorly planned kitchens within the first year. You’ll need to engineer solutions for thermal bridging, differential expansion, and microclimate control to prevent structural failure and create a functional cooking environment.
Extreme temperature swings from freezing winters to 120°F+ summer cooking sessions create thermal stress that cracks countertops, warps cabinet doors, and loosens fasteners if not properly engineered during construction. I’ve watched homeowners spend thousands replacing cracked granite countertops that split along expansion joints that were never planned for.
Different materials expand at dramatically different rates – steel expands twice as fast as concrete, creating destructive stress points at connection joints that require calculated expansion gaps and flexible sealants. When you ignore these expansion rates, your beautiful DIY outdoor kitchen turns into a maintenance nightmare within months.
Pre-Construction Thermal Assessment Checklist
-
☐ Calculate thermal expansion rates for all material combinations
-
☐ Map solar exposure patterns across all seasons using sun path diagrams
-
☐ Identify prevailing wind directions and seasonal variations
-
☐ Plan thermal break locations at all metal-to-masonry connections
-
☐ Size expansion joints based on maximum expected temperature differentials
-
☐ Select sealants rated for local temperature extremes (-40°F to 400°F+)
-
☐ Design ventilation openings based on BTU output calculations
-
☐ Plan condensation collection and drainage points
-
☐ Specify thermal barrier materials for high-heat zones
Heat Management Beyond the Obvious
Your DIY outdoor kitchen develops a complex thermal ecosystem where radiant heat, convection currents, and conductive heat transfer interact in ways that can make your space unusable or dangerous. Understanding these heat patterns determines appliance placement, material selection, and structural design decisions that separate functional kitchens from expensive failures.
Heat doesn’t just radiate upward from cooking surfaces – it reflects off walls, bounces under counters, and creates hot spots in unexpected locations that can burn users or damage equipment. I’ve seen cabinet handles become untouchable because reflected heat concentrated in areas the builder never considered during planning.
Thermal bridging through metal components creates invisible heat highways where a grill’s 500°F heat travels through steel framing to make cabinet handles untouchable. Proper heat management requires mapping thermal zones during design phase, not discovering problems after construction when fixes become expensive retrofits.
|
Material |
Thermal Expansion Rate (inches per 100°F per foot) |
Heat Conductivity |
Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Steel |
0.0065 |
High |
Structural framing with thermal breaks |
|
Concrete |
0.0055 |
Low |
Foundations, countertops |
|
Stainless Steel |
0.0096 |
High |
Appliances, work surfaces |
|
Natural Stone |
0.0044 |
Low |
Countertops, flooring |
|
Aluminum |
0.0128 |
Very High |
Avoid in high-heat zones |
Thermal Bridging in Metal Frame Construction
Metal studs and frames act as heat conductors that transfer dangerous temperatures throughout your DIY outdoor kitchen frame structure. Without thermal breaks, a hot grill can make cabinet handles, countertop edges, and structural components too hot to touch safely. This invisible heat transfer also accelerates material degradation and creates liability issues.
Stainless steel framing conducts heat so efficiently that 500°F grill temperatures can make cabinet hardware 150°F+ within minutes of cooking. Thermal breaks using ceramic fiber blankets and high-temperature foam strips interrupt heat conduction at critical junction points.
Nylon washers and thermal gaskets at fastener locations prevent heat transfer while maintaining structural integrity. Strategic placement of thermal barriers during framing stage costs pennies compared to retrofitting solutions after discovering heat problems.
A London homeowner learned this lesson the hard way when building their DIY outdoor kitchen. As reported by House Beautiful, Daniel Cox “actually broke my hand in four places while building the outdoor kitchen” due to inexperience with power tools, but the project’s £4,000 budget success demonstrates how proper planning can overcome setbacks.
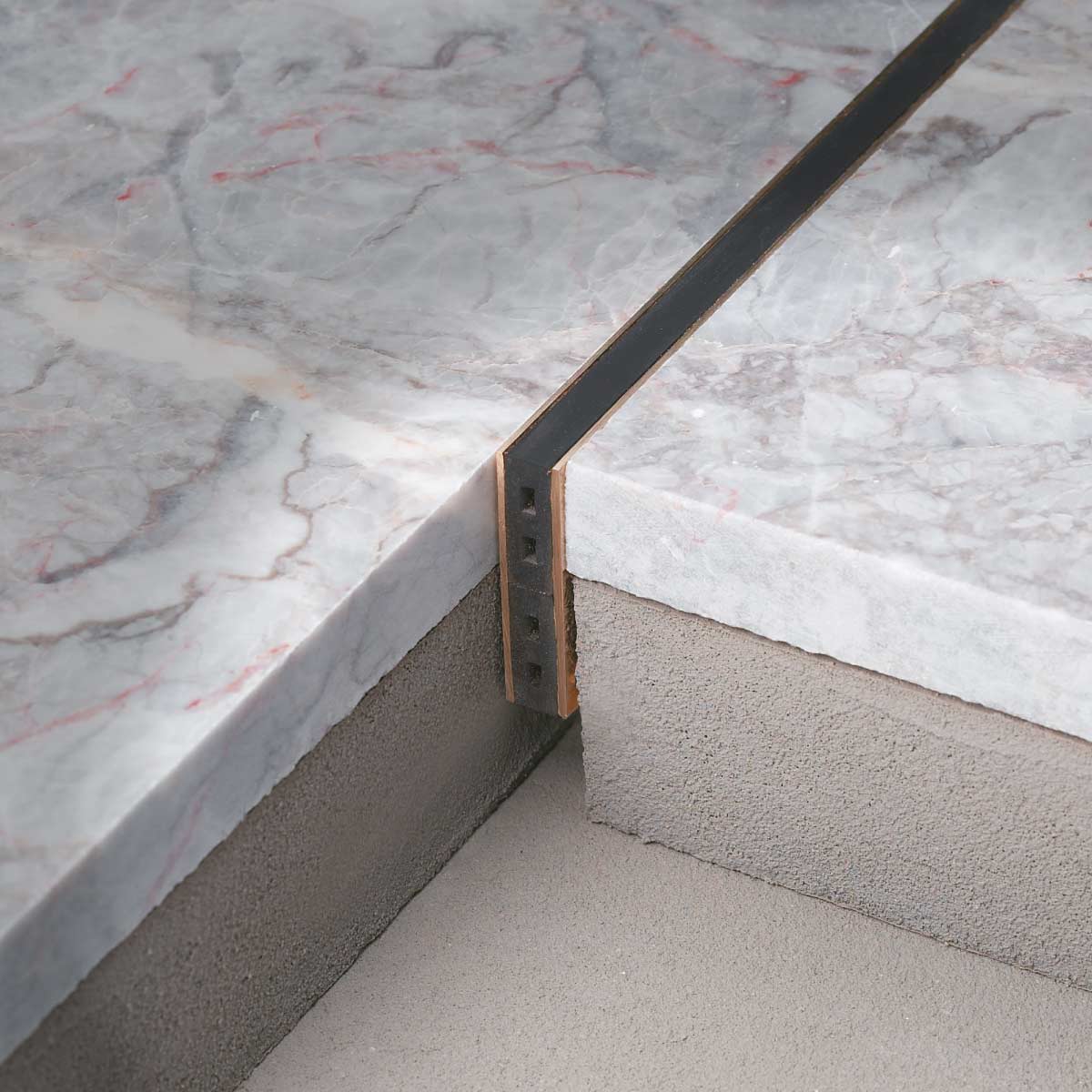
Differential Expansion Planning
Every material in your outdoor kitchen expands and contracts at different rates as temperatures change. Concrete, steel, stone, and wood all move differently, creating stress points that crack surfaces, loosen connections, and destroy structural integrity. Planning for these movements during design prevents catastrophic failures.
Steel expands 0.0065 inches per foot per 100°F temperature change, while concrete only expands 0.0055 inches – this difference destroys rigid connections. Expansion joints every 8-10 feet in continuous surfaces allow materials to move without creating destructive stress concentrations.
Flexible sealants rated for temperature extremes (typically -40°F to 400°F+) accommodate movement while maintaining weather sealing. Material transition points require calculated gaps and flexible connections rather than rigid attachments that transfer expansion stress.
Microclimate Creation and Control
Your outdoor kitchen creates its own localized weather system through heat generation, air circulation patterns, and humidity production. This microclimate affects food safety, structural durability, and user comfort in ways that require intentional design solutions rather than hoping natural ventilation will handle the problems.
Cooking generates massive amounts of steam, grease-laden vapor, and radiant heat that create humidity levels and air temperatures dramatically different from surrounding outdoor conditions. Poor microclimate control leads to mold growth, accelerated corrosion, dangerous heat buildup, and unusable cooking conditions during peak hours.
Strategic ventilation design, moisture management systems, and heat reflection control create comfortable, safe, and durable outdoor cooking environments.
Convection Current Mapping
Hot air movement through your outdoor kitchen determines whether heat dissipates safely or creates dangerous buildup zones. Understanding convection patterns during design allows optimal appliance placement and prevents enclosed areas from becoming heat traps that damage equipment or injure users.
Hot air rises predictably, but outdoor wind patterns, overhead structures, and nearby buildings create complex air circulation that requires analysis during design phase. Smoke stick testing during initial planning reveals air flow patterns that determine ventilation requirements and appliance positioning.
Passive ventilation openings must be sized and positioned based on BTU output calculations, not guesswork about “adequate airflow.” Intentional air gaps in overhead structures prevent heat trapping while maintaining weather protection and structural integrity.
Humidity Buffer Zones
Outdoor cooking generates enormous amounts of moisture that must be managed to prevent mold, rust, and structural damage. Creating graduated moisture protection zones from high-exposure cooking areas to protected storage spaces prevents humidity-related failures while maintaining functionality.
Steam production from grills, side burners, and cleaning activities creates humidity levels that exceed indoor bathroom conditions during cooking sessions. Moisture-resistant materials must be selected and installed in graduated systems – marine-grade stainless near cooking zones, weather-resistant wood in protected areas.
Condensation collection points require designed drainage systems rather than hoping moisture will evaporate before causing damage. Strategic vapor barrier placement prevents moisture trapping while allowing necessary drying – universal vapor barriers often create more problems than they solve.
Radiant Heat Reflection Management
Reflected heat from surfaces creates cooking dead zones or dangerously hot areas that make your kitchen unusable during peak sun hours. Managing radiant heat through surface selection, shade structures, and strategic positioning ensures your kitchen remains functional throughout the day and across seasons.
Polished stainless steel and light-colored surfaces reflect radiant heat in concentrated beams that can exceed direct sun temperatures by 20-30°F. Solar path calculators reveal seasonal sun angle changes that affect radiant heat patterns – summer and winter heat reflection patterns differ dramatically.
Adjustable shade structures with reflective undersides provide flexible heat control while maintaining natural lighting for food preparation. Textured surfaces scatter reflected heat rather than concentrating it, reducing hot spot formation while maintaining easy cleaning properties.
The Psychology of Outdoor Cooking Workflow
Outdoor cooking involves completely different human behavior patterns than indoor kitchen work. Weather conditions, social dynamics, lighting changes, and seasonal variations require design approaches that accommodate these behavioral differences rather than applying indoor kitchen principles to outdoor spaces. Understanding these psychological factors helps inform outdoor kitchen ideas that actually work in practice.
When planning your outdoor cooking space, consider how garage clean-out services can help clear storage areas for seasonal cooking equipment and supplies that support year-round outdoor kitchen functionality.
Traditional kitchen work triangles fail outdoors where wind, sun glare, and social interactions change how people move through cooking tasks. Seasonal daylight variations and weather conditions require flexible design solutions that adapt to changing behavioral patterns throughout the year.
Behavioral Pattern Recognition
People move, cook, and socialize differently in outdoor environments where weather, lighting, and social dynamics create unique behavioral patterns. Successful outdoor kitchen design accommodates these natural behaviors rather than forcing users to adapt to inappropriate indoor design principles.
Wind affects movement patterns, cooking techniques, and social positioning in ways that require multiple pathway options and flexible work zone configurations. Outdoor cooking naturally becomes social activity where guests want to participate or observe, creating traffic patterns that don’t exist in indoor kitchens.
Weather-dependent behavior changes require design flexibility that allows the space to function effectively across different environmental conditions.
Educational institutions are recognizing the value of hands-on outdoor kitchen construction. “Three Forks High School students build outdoor kitchen” KBZK reports, where students are learning construction skills while building functional outdoor cooking spaces, demonstrating how practical experience enhances traditional classroom learning.
Weather-Dependent Traffic Flow
Wind, rain, and intense sun dramatically change how people move through outdoor cooking spaces. Designing multiple pathway options and flexible work zones accommodates these weather-driven behavior changes rather than creating bottlenecks during challenging conditions.
Strong winds force people to approach cooking areas from sheltered directions and seek protected prep spaces, requiring multiple access routes to key work zones. Rain and intense sun create natural gathering spots under covered areas, concentrating foot traffic in ways that require wider pathways and flexible furniture arrangements.
Seasonal wind pattern changes mean summer and winter traffic flows follow different routes through the same space. Adjustable wind barriers and removable shade structures allow the kitchen layout to adapt to prevailing weather conditions rather than fighting environmental forces.
Social Gravity Points
Outdoor kitchens naturally attract social interaction, but poor planning creates bottlenecks that exclude participants or interfere with cooking efficiency. Strategic design creates comfortable observation zones and multiple activity centers that distribute social pressure while maintaining cooking functionality.
Cooking activities outdoors draw spectators who want to participate or observe, requiring designated “lean zones” where guests can engage without interfering with work flow. Single-focus designs create social bottlenecks where everyone crowds around one activity, while multiple activity centers distribute engagement across the space.
Ambient lighting placement influences where people naturally gather, allowing designers to direct social flow toward desired areas. Counter height variations and strategic seating placement create natural social hierarchies that separate active participants from casual observers.
Seasonal Adaptation Strategies
Outdoor kitchens must transform functionality across seasons while maintaining structural integrity and usability. Building in seasonal adaptability from the start allows your kitchen to evolve with changing needs and weather conditions without requiring major reconstruction projects.
Seasonal daylight changes affect both functional lighting needs and social atmosphere, requiring layered lighting systems with independent controls. Modular design approaches allow seasonal additions and modifications without compromising the core kitchen structure or requiring permit modifications.
Modular Component Systems
Building modularity into your outdoor kitchen from the start allows seasonal modifications and future expansions without major reconstruction. Standardized connection points and weatherproof storage for seasonal components provide flexibility while maintaining structural integrity.
Standardized mounting systems allow easy swapping of seasonal components like heaters, wind screens, and extended prep surfaces without requiring tools or structural modifications. Pre-planned connection points for utilities (electrical, gas, water) support seasonal additions while maintaining code compliance and safety standards.
Weatherproof storage integrated into the kitchen structure keeps seasonal components protected and easily accessible when needed. Modular design prevents the need for permanent installations that may violate setback requirements or trigger additional permit requirements.
Lighting Psychology Across Seasons
Outdoor lighting needs change dramatically with seasonal daylight patterns, affecting both cooking functionality and social atmosphere. Layered lighting systems with warm color temperatures counteract seasonal mood effects while providing adequate task illumination across varying conditions.
Winter’s shorter days require earlier artificial lighting activation, while summer cooking extends well into natural twilight hours, demanding flexible lighting control systems. Warm-temperature LEDs (2700K-3000K) counteract the psychological effects of reduced winter daylight and create inviting social atmospheres during shoulder seasons.
Motion-activated safety lighting provides security and functionality during off-season use without requiring manual activation of full lighting systems. Layered lighting with independent controls allows customization for different activities – bright task lighting for food prep, ambient lighting for social gatherings, accent lighting for aesthetic appeal.
Infrastructure Integration and Hidden Utilities
The most challenging aspect of DIY outdoor kitchen construction involves the complex underground utility systems, drainage solutions, and structural engineering that must function flawlessly in harsh outdoor conditions. These hidden systems determine long-term success more than visible design elements.
Major utility installations often generate substantial debris removal that requires professional removal to maintain safe working conditions during your outdoor kitchen build.
Underground utility planning requires thinking beyond immediate needs to accommodate future expansions, maintenance access, and emergency shutoffs without demolishing existing structures. Structural load calculations for outdoor kitchens must account for dynamic forces from wind, seismic activity, and thermal expansion that don’t affect indoor construction.
Utility Corridor Design
Creating dedicated pathways for all utilities prevents future conflicts and allows upgrades without demolishing existing structures. Proper corridor design accommodates multiple utility types while providing maintenance access and expansion capability.
Mapping existing underground utilities using professional locating services prevents expensive damage and ensures new installations don’t conflict with established infrastructure. Dedicated utility trenches with standardized depths and separation distances meet code requirements while simplifying future maintenance and expansion projects.
Excess capacity planning (typically 50% additional space) accommodates future electrical circuits, gas lines, or water connections without requiring new excavation. Access points and pull strings every 25 feet allow cable and pipe installation or replacement without excavating entire utility runs.
Utility Installation Safety Protocol
-
☐ Call 811 for professional utility location services
-
☐ Obtain all required excavation permits
-
☐ Plan trenches with 50% excess capacity for future expansion
-
☐ Install pull strings and access boxes every 25 feet
-
☐ Size electrical service for peak demand plus 25% safety margin
-
☐ Install GFCI protection on all outdoor electrical circuits
-
☐ Plan gas line pressure testing and inspection schedule
-
☐ Design drainage system for 100-year flood capacity
-
☐ Install emergency shutoffs in accessible locations
-
☐ Document all underground installations with GPS coordinates
Underground Utility Orchestration
Proper utility planning requires comprehensive coordination of electrical, gas, water, and drainage systems with adequate capacity for future expansion and maintenance access. Poor utility design creates expensive problems that require demolition to fix, while proper planning provides decades of trouble-free operation.
Professional utility locating services prevent costly damage to existing underground infrastructure and ensure compliance with safety regulations during excavation. Utility trenches designed with 50% excess capacity accommodate future additions without requiring new excavation or disrupting existing systems.
Pull strings and access points every 25 feet allow maintenance and upgrades without excavating entire utility runs.
A DIY outdoor kitchen project can achieve professional results through strategic planning and phased construction. According to This Old House, “DIYing your outdoor kitchen can save you an average of 20%–40% or $1,500–$6,000 in labor fees,” transforming a $20,000 professional installation into a $12,000-$16,000 DIY project while maintaining quality through proper utility planning.
Greywater and Stormwater Management
Outdoor kitchens generate significant wastewater that requires proper management to prevent environmental problems and code violations. Integrated drainage systems must handle both kitchen wastewater and stormwater runoff while meeting local environmental regulations.
Grease traps sized for specific cooking appliances prevent drain blockages and environmental contamination while meeting local wastewater regulations. Infiltration systems designed for both kitchen wastewater and stormwater runoff prevent flooding while protecting groundwater quality.
Overflow protection systems handle extreme weather events that exceed normal drainage capacity, preventing property damage and environmental violations. Proper greywater management often reduces overall utility costs while meeting increasingly strict environmental regulations in many jurisdictions.
|
Drainage System Component |
Capacity Requirements |
Maintenance Frequency |
Code Compliance Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Grease Trap |
2x peak flow rate |
Monthly cleaning |
Required for commercial-style equipment |
|
Floor Drains |
1 per 150 sq ft |
Quarterly inspection |
Must connect to approved drainage |
|
Overflow Protection |
150% of design capacity |
Annual testing |
Required in flood-prone areas |
|
Infiltration Basin |
Site-specific calculation |
Bi-annual maintenance |
Environmental permit may be required |
Structural Load Path Engineering
Outdoor kitchen structures must handle static loads from appliances and countertops plus dynamic loads from wind, seismic activity, and thermal expansion. Proper load path engineering ensures forces transfer safely through the entire structure to the foundation without creating failure points.
Wind loads on outdoor structures create uplift forces and lateral loads that can destroy improperly designed kitchens, requiring calculations based on local building codes and site-specific exposure factors. Load path engineering ensures forces transfer through the entire structure to the foundation rather than concentrating stress at connection points that can fail catastrophically.
Wind Load Distribution
Wind affects outdoor structures differently than enclosed buildings, creating uplift forces and lateral loads that require specific engineering solutions. Proper wind load analysis and connection design prevent structural failure during severe weather events.
Local building codes provide wind load calculations based on geographic location and site exposure, but outdoor kitchen structures often experience higher loads than standard residential construction. Connection details must transfer wind loads through the entire structure to the foundation rather than relying on individual fasteners to resist uplift and lateral forces.
Temporary bracing systems during construction prevent progressive collapse before permanent connections are completed and load paths are established. Overhead structures like pergolas and shade covers create significant wind loads that require engineered connections and proper foundation design to prevent failure.
Budget-Conscious Innovation Through Strategic Salvage
The most successful budget outdoor kitchens aren’t built with cheap materials, but with strategically sourced, repurposed, and modified commercial and industrial components that outperform residential alternatives. Restaurant equipment liquidations, construction waste streams, and industrial surplus provide high-quality materials at fraction of retail costs while delivering superior durability and functionality for your DIY outdoor kitchen on a budget.
Strategic material sourcing often requires clearing existing outdoor spaces of old equipment and debris. Professional scrap metal removal services can efficiently clear valuable salvageable materials while properly disposing of unusable components.
Commercial kitchen equipment offers superior performance and durability compared to residential outdoor appliances, but requires strategic modifications to maintain warranty coverage while adding weather protection. Construction waste streams and industrial surplus generate high-quality materials that often exceed the performance of purpose-built outdoor kitchen components when properly sourced and integrated.
Commercial Equipment Adaptation
Restaurant and institutional equipment, when properly modified, offers superior performance and durability at fraction of the cost of outdoor-rated residential appliances. Strategic sourcing from liquidations and auctions provides professional-grade functionality while weatherization modifications ensure long-term outdoor performance.
Restaurant supply liquidations and auctions provide access to commercial-grade equipment at 20-30% of retail cost, often with minimal wear from failed restaurant ventures. Weatherproof enclosures using marine-grade materials protect commercial equipment while maintaining ventilation requirements and warranty compliance.
Commercial equipment integration requires upgrading electrical connections to outdoor-rated standards while preserving equipment grounding and safety systems.
Natural stone remains the preferred choice for outdoor countertops, selected by 57% of homeowners according to the National Kitchen and Bath Association, followed by quartz at 23%, demonstrating the demand for durable materials that can withstand outdoor conditions.
Food Service Equipment Weatherization
Commercial kitchen equipment can be adapted for outdoor use through strategic modifications that maintain warranty coverage while adding weather protection. Marine-grade enclosures and upgraded electrical connections transform restaurant equipment into weather-resistant outdoor appliances.
Restaurant supply liquidations provide access to barely-used commercial equipment from failed ventures, often at 70-80% below retail pricing for equivalent outdoor-rated residential models. Marine-grade materials and ventilation systems create weatherproof enclosures that protect commercial equipment while maintaining manufacturer warranty requirements.
Electrical connection upgrades to outdoor-rated standards ensure safety and code compliance while preserving equipment grounding systems. Strategic modification approaches maintain equipment serviceability and parts availability compared to purpose-built outdoor appliances with limited service networks.
Industrial Shelving and Storage Systems
Commercial wire shelving and stainless steel work tables provide superior functionality and can be integrated into custom cabinetry systems. Industrial-grade components offer better durability and flexibility than residential outdoor kitchen storage solutions while costing significantly less, making them ideal for DIY outdoor kitchen cabinets.
Commercial wire shelving systems provide superior ventilation and drainage compared to enclosed residential cabinetry, preventing moisture buildup and extending component life. Stainless steel work tables from restaurant closures offer food-safe surfaces and integrated storage at costs well below custom outdoor cabinetry.
Commercial casters and leveling systems allow moveable components that adapt to seasonal needs while maintaining stability during use. Industrial drainage systems integrated into work surfaces provide functionality that residential outdoor sinks can’t match.
Material Recovery and Upcycling Strategies
Construction waste streams and industrial surplus provide high-quality materials that often exceed the performance of purpose-built outdoor kitchen components. Developing relationships with demolition contractors and learning to assess salvaged materials creates access to premium building materials at minimal cost.
Demolished buildings and landscaping projects generate massive amounts of reusable stone, brick, and concrete that can form the structural backbone of outdoor kitchen construction. Strategic relationships with demolition contractors and landscape companies provide access to premium materials before they reach waste streams.
The outdoor kitchen market reflects diverse fuel preferences, with 44% using propane, 45% connecting to natural gas, and 22% preferring charcoal according to Interior Design, highlighting the importance of flexible utility planning that can accommodate different cooking preferences.
Masonry and Stone Recovery
Demolished buildings and landscaping projects generate massive amounts of reusable stone, brick, and concrete that can form the backbone of outdoor kitchen construction. Learning to assess structural integrity and contamination in salvaged masonry provides access to premium materials while developing flexible construction details accommodates irregular salvaged components.
Demolition contractors and landscape companies generate consistent streams of high-quality masonry materials that cost pennies compared to quarried stone and new brick. Structural integrity assessment techniques identify sound masonry materials while screening out damaged or contaminated components that could compromise construction quality.
Flexible construction details accommodate irregular salvaged materials while maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Contamination screening prevents incorporation of materials with lead paint, asbestos, or chemical contamination that could create health hazards.
Strategic material sourcing can dramatically reduce costs while improving quality. A successful DIY approach involves identifying high-quality salvaged materials from construction waste streams, such as natural stone from landscaping renovations or commercial-grade stainless steel from restaurant closures, which often provide superior durability compared to residential outdoor kitchen components at fraction of the cost.
Regulatory Navigation and Code Compliance Strategies
The regulatory landscape for outdoor kitchens exists in a gray area where residential, commercial, and agricultural codes intersect, creating opportunities for creative compliance that can save thousands while ensuring safety. Understanding permit triggers and classification definitions allows strategic construction phasing that minimizes bureaucratic complications, making what seems complex into an easy DIY outdoor kitchen project.
Complex outdoor kitchen projects often require professional debris removal services to maintain code compliance with construction site cleanliness requirements and proper disposal of regulated materials.
Permit pathway optimization involves understanding which construction activities trigger additional requirements, allowing strategic phasing that minimizes regulatory complications. Insurance optimization through proper documentation and construction methods can reduce premiums while providing better coverage than standard homeowner policies.
Permit Pathway Optimization
Understanding which permits trigger additional requirements allows you to phase construction in ways that minimize bureaucratic complications and associated costs. Strategic classification of structures and electrical installations can dramatically affect approval processes and inspection schedules.
Electrical service classification between temporary and permanent installations affects permit requirements and inspection schedules in ways that can streamline approval processes. Structural versus accessory building definitions determine which building codes apply and can mean the difference between simple and complex approval processes.
Square footage thresholds and building separation strategies can avoid triggering commercial kitchen codes that dramatically increase compliance costs.
The trend toward sophisticated outdoor kitchens continues growing, with luxury features becoming standard. “Country and Town House” reports that “clients are pushing the boundaries with their outdoor kitchens” including “built-in grills and super-sized seating areas with gazebos and log burners, not to mention outdoor televisions, bars and heating,” demonstrating how regulatory planning must accommodate increasingly complex installations.
Electrical Service Classification Gaming
The distinction between temporary and permanent electrical installations can dramatically affect permit requirements and inspection schedules. Strategic use of portable distribution panels and plug-in appliances during construction phases minimizes regulatory complexity while maintaining safety standards.
Temporary electrical service using portable distribution panels avoids permanent installation permit requirements during construction phases, simplifying approval processes. Plug-in appliance configurations initially avoid hardwired installation requirements that trigger additional inspections and code compliance measures.
Conversion to permanent service after other inspections are complete prevents cascading permit modifications that can delay project completion. Portable electrical systems maintain safety standards while providing flexibility during construction and early operation phases.
Structural vs. Accessory Building Definitions
How your outdoor kitchen is classified determines which building codes apply and can mean the difference between simple and complex approval processes. Creating separate accessory structures rather than one large building and using moveable components can avoid permanent construction classifications.
Square footage thresholds that trigger commercial kitchen codes can be avoided through strategic design of multiple smaller structures rather than single large buildings. Separate accessory structures often fall under simplified approval processes compared to additions or primary structures that require full architectural review.
Moveable components that don’t constitute permanent construction avoid many building code requirements while providing full functionality. Strategic use of temporary and semi-permanent construction techniques maintains functionality while avoiding regulatory triggers that increase costs and complexity.
Insurance and Liability Optimization
Proper documentation and construction methods can actually reduce insurance premiums while providing better coverage than standard homeowner policies. Strategic use of professional consultants for specific aspects transfers liability while maintaining DIY cost savings on labor-intensive work.
Documentation strategies during construction provide evidence of proper installation methods that insurance companies reward with premium discounts for outdoor kitchen coverage. Strategic professional consultation for critical systems transfers liability while maintaining DIY cost savings on labor-intensive construction work.
Documentation for Premium Reduction
Insurance companies offer significant discounts for outdoor kitchens that meet specific safety standards, but only if properly documented during construction. Photographic records of concealed work and third-party inspections provide evidence that reduces premiums while ensuring proper installation.
Photographic documentation of all concealed work before closing up walls or trenches provides evidence of proper installation that insurance companies require for premium discounts. Detailed material specifications and installation records demonstrate compliance with manufacturer requirements and building codes that affect liability coverage.
Third-party inspections for critical systems, even when not required by code, provide professional verification that reduces insurance company risk assessments. Proper documentation often pays for itself through reduced insurance premiums over the first few years of operation.
Liability Transfer Through Professional Consultation
Strategic use of professional consultants for specific aspects can transfer liability while maintaining DIY cost savings on labor-intensive work. Hiring professionals for design and critical connections while performing installation work yourself optimizes both cost and risk management.
Structural engineers for foundation and framing design transfer liability for critical load-bearing elements while allowing DIY installation of their engineered plans. Licensed electricians for service connections and main panel work transfer liability for the most dangerous electrical work while allowing DIY branch circuit installation.
Professional gas line installations handle the highest-risk utility connections while allowing DIY appliance connections and minor modifications. Strategic professional consultation provides liability protection and code compliance verification while maintaining significant cost savings on labor-intensive construction tasks.
Clearing construction debris, old appliances, and landscaping waste becomes a major challenge during outdoor kitchen projects. The strategic salvage approaches we’ve discussed require reliable waste removal for materials you can’t use, while construction phases generate substantial debris that must be managed safely.
For major renovation projects, understanding construction waste disposal options ensures compliance with local regulations while maintaining efficient project timelines throughout your outdoor kitchen build.
Jiffy Junk’s environmentally responsible approach aligns perfectly with the sustainable building practices that make budget-conscious outdoor kitchens successful. Their sorting and recycling services ensure your construction waste becomes part of a circular economy rather than heading to landfills. When you’re sourcing commercial equipment or salvaged materials, they can clear unusable items from estate sales or demolition sites, letting you focus on selecting the best components.
The White Glove Treatment keeps your property organized throughout complex utility installations and staged construction that outdoor kitchens require. Rather than letting debris create safety hazards, regular removal maintains the precise working conditions that thermal management and structural engineering demand.
Professional appliance removal services become essential when replacing indoor appliances with outdoor-rated equipment or clearing space for new installations during your kitchen transformation.
Ready to tackle your outdoor kitchen project with professional waste management support? Contact Jiffy Junk today to discuss how their services can streamline your construction process while supporting your sustainable building goals.
Final Thoughts
Building a successful DIY outdoor kitchen requires understanding complex systems that most guides completely ignore. Thermal dynamics, behavioral psychology, hidden infrastructure, strategic material sourcing, and regulatory navigation determine long-term success far more than surface-level design decisions. The Pinterest-perfect images don’t show the engineering challenges, code compliance strategies, or innovative sourcing techniques that separate functional outdoor kitchens from expensive failures.
Your outdoor kitchen will create its own microclimate, generate substantial waste streams, and require utility systems that exceed typical residential construction complexity. Success comes from planning for these realities during design rather than discovering problems after construction when solutions become exponentially more expensive.
Successful DIY outdoor kitchens require engineering-level planning for thermal management, utility coordination, and structural loads that typical residential construction doesn’t encounter. Strategic material sourcing and regulatory navigation can reduce total project costs by 60-70% while delivering superior performance compared to conventional residential outdoor kitchen approaches.
Long-term success depends on understanding the complex interactions between thermal dynamics, human behavior, infrastructure systems, and regulatory requirements that determine functionality and durability over decades of use.